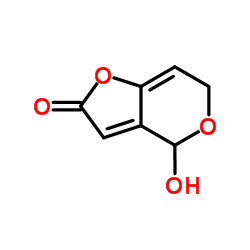
9001-37-0
| Name | Oxidase glucose |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
beta-D-Glucose:quinone oxidoreductase
(2,4-Dihydroxy-2H-pyran-3(6H)-ylidene)acetic Acid 3,4-Lactone Alfamalt Gloxyl 4080 DL-Patulin Mycoin C3 beta-D-Glucose oxidase Clavacin Claviformin EINECS 232-601-0 Penicidin Clairformin Patulin Bakezyme G01500 gigantin MFCD00131182 Clavatin Patuline Claviform 4-Hydroxy-4H-furo[3,2-c]pyran-2(6H)-one |
| Description | Glucose oxidase is used in the food and beverage industry as a preservative and stabilizer and is commonly derived from the fungus Aspergillus niger. Glucose oxidase can react with intracellular glucose and oxygen (O2) to produce hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and gluconic acid, which can cut off the nutrition source of cancer cells and consequently inhibit their proliferation[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Microbial Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Glucose oxidase is a subset of oxidoreductase enzymes that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from an oxidant to a reductant. Glucose oxidases use oxygen as an external electron acceptor that releases hydrogen peroxide (H2 O2). Glucose oxidase has many applications in commercial processes, including improving the color and taste, increasing the persistence of food materials, removing the glucose from the dried egg, and eliminating the oxygen from different juices and beverages[4]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 513.7±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C6H12O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 154.120 |
| Flash Point | 226.8±23.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 154.026611 |
| LogP | -0.75 |
| Appearance | solution (clear) | yellow |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.603 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H334 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P342 + P311 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn,Xi |
| Risk Phrases | 42-36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 45-22-23-36-26-24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | RQ8452000 |
| HS Code | 35079090 |