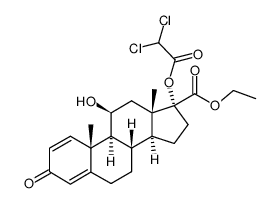
199331-40-3
| Name | etiprednol dicloacetate |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
etiprednol dichloroacetate
EDA BNP-166 (8S,9S,10R,11S,13S,14S,17R)-17-(2,2-Dichloro-acetoxy)-11-hydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-3-oxo-6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-17-carboxylic acid ethyl ester etiprednol dichloacetate ethyl 17α-dichloroacetoxy-11β-hydroxyandrosta-1,4-dien-3-one-17β-carboxylate |
| Description | Etiprednol dicloacetate (BNP 166) is an anti-inflammatory agent. Etiprednol dicloacetate inhibits eosinophil accumulation. Etiprednol dicloacetate can be used in the research of inflammatory airway diseases, such as asthma[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Etiprednol dicloacetate (1 nM-1 μM) inhibits LPS-induced TNF-α production by human blood[1]. |
| In Vivo | Etiprednol dicloacetate (0-100 μg/kg, intranasal inhalation) attenuates peribronchial eosinophilia in the lung of the allergen sensitized and challenged rats[1]. Etiprednol dicloacetate (0.1 μg/kg, intranasal inhalation) inhibits eosinophil accumulation in rats (antigen-induced airway eosinophil infiltration)[3]. Etiprednol dicloacetate (0-20 mg/kg, p.o., 28 days) is well tolerated in rats and dogs[2]. Animal Model: Allergen sensitized and challenged Brown Norway rats[1] Dosage: 0.1, 1, 10, and 100 μg/kg Administration: Intranasal inhalation Result: Decreased the number of eosinophils at the perivascular area of the lung tissue. Decreased the number of mucus secreting cells and antigen-induced formation of perivascular edema. |
| Molecular Formula | C24H30Cl2O6 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 485.39700 |
| Exact Mass | 484.14200 |
| PSA | 89.90000 |
| LogP | 3.91390 |