782487-28-9
| Name | Rosiptor |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
6R5034F862
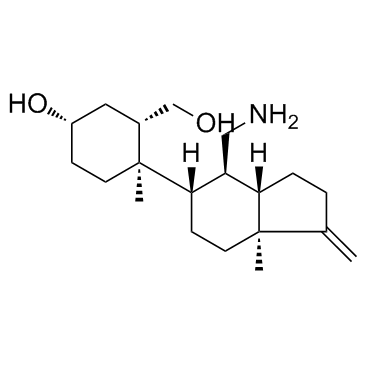
rosiptor (1S,3S,4R)-4-[(3aS,4R,5S,7aS)-4-(Aminomethyl)-7a-methyl-1-methyleneoctahydro-1H-inden-5-yl]-3-(hydroxymethyl)-4-methylcyclohexanol UNII:6R5034F862 |
| Description | Rosiptor is an activator of SH2-containing inositol-5'-phosphatase 1 (SHIP1). |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
SHIP1[1] |
| In Vitro | Rosiptor is a small-molecule SHIP1 activator.The activating effect of Rosiptor on SHIP1 is 28% at 100 μM in the native enzyme but no effect of Rosiptor is observed when the SHIP1ΔC2 enzyme is used. Rosiptor induces a concentration-dependent decrease in Akt phosphorylation in MOLT-4 cells, while it fails to affect Akt phosphorylation in Jurkat cells. At 0.1 μM Rosiptor the inhibition amounts to an average of 34%, while at 10 μM the inhibition amounts to an average of 82% in two independent experiments. Rosiptor also induces a concentration-dependent decrease in the production of multiple pro-inflammatory mediators in this system, without affecting cell viability. Rosiptor dose dependently inhibits chemotaxis of most cell types at low micromolar concentrations independent of the chemotactic stimulus[1]. |
| In Vivo | In female Sprague-Dawley rats, the single-dose pharmacokinetics of Rosiptor show that the increases in maximal plasma concentration (Cmax) and AUC0-∞ are dose-proportional at the lower end of the dosing regimen and greater than dose proportional at the higher doses. The oral bioavailability of Rosiptor in rats is 66 and 85% at 10 and 30 mg/kg respectively. Oral bioavailability of Rosiptor in dogs is 88 and 104% at 10 and 30 mg/kg respectively. High tissue concentrations of Rosiptor are detected, as compared to plasma concentrations, at each time point studied[1]. |
| Kinase Assay | To study enzyme kinetics using either IP4 or diC8-PI(3,4,5)P3 (diC8-PIP3) as substrates, enzyme activity over time is measured in the absence or presence of Rosiptor and varying concentrations of IP4 or diC8-PIP3. Phosphate released at each substrate concentration is plotted against time, and initial velocities are determined and plotted against IP4 or diC8-PIP3 concentration[1]. |
| Cell Assay | Bone marrow cells are obtained from 4- to 8-week-old SHIP1+/+ and SHIP1-/- mice and bone marrow-derived mast cells (BMMCs) are prepared. Mast cells are sensitized overnight with anti-DNP IgE (SPE-7). Cells are then washed and incubated in the presence of vehicle control (media only) or Rosiptor (60 μM) prior to stimulation with the indicated concentration of DNP-human serum albumin (DNP-HSA), followed by the measurement of β-hexosaminidase from the culture supernatant[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Female Sprague-Dawley rats and beagle dogs (male and female) are treated with Rosiptor in saline by bolus i.v. injection (at 1 mL/kg ) or by oral gavage (at 5 mL/kg). Blood is sampled 0 to 48 h post-dose and plasma isolated. Plasma concentrations of Rosiptor are quantified using a validated HPLC-MS/MS method. Pharmacokinetic parameters are determined by non-compartmental analysis[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 451.6±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C20H35NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 321.497 |
| Flash Point | 226.9±28.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 321.266785 |
| LogP | 3.34 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.547 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |