808732-98-1
| Name | Rislenemdaz |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
UNII:5HAM167S5T
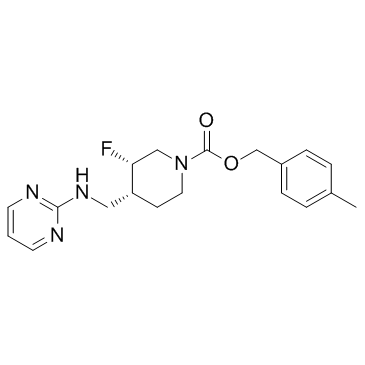
MFCD14635204 Rislenemdaz 1DY7M91WQ1 4-Methylbenzyl (3S,4R)-3-fluoro-4-[(2-pyrimidinylamino)methyl]-1-piperidinecarboxylate (-)-(3S,4R)-4-Methylbenzyl-3-fluoro-4-((pyrimidin-2-ylamino)methyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate 5HAM167S5T |
| Description | Rislenemdaz (CERC-301) is an orally bioavailable and selective N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor subunit 2B (GluN2B) antagonist with Ki and IC 50 of 8.1 nM and 3.6 nM, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 3.6 nM (GluN2B)[1] Ki: 8.1 nM (GluN2B)[1] |
| In Vitro | Rislenemdaz (CERC-301) inhibits calcium influx into agonist-stimulating NMDA-GluN1a/GluN2B L(tk-) cells with an IC50 of 3.6 nM. Rislenemdaz exhibits at least 1000× selectivity for the GluN2B receptor versus all targets tested, including the hERG potassium channel. Rislenemdaz also exhibits minimal activity against sigma-type receptors at 10 uM[1]. |
| In Vivo | Rislenemdaz (CERC-301) (1, 3, 10, and 30 mg/kg) significantly decreases immobility frequency (P<0.001) and significantly increases swimming behavior (P<0.01 for 1, 3, and 30 mg/kg; P<0.05 for 10 mg/kg) compare to the vehicle control. Rislenemdaz plasma levels are approximately 15, 120, 390, 1420, 4700, and 14,110 nM (0.015, 0.120, 0.390, 1.42, 4.7, and 14.11 uM) at the time of sampling, corresponding to approximately 5, 29, 56, 83, 94, and 98% RO, respectively, in rats. The ED50 for increaing in frequency of swimming and decreasing in immobility are ~0.3 and 0.7 mg/kg, respectively, corresponding to RO of ~30 and 50%. Rislenemdaz (1, 3, 10, and 30 mg/kg) significantly increases total distance traveling (P<0.01 for 1 mg/kg; P<0.001 for 3, 10, and 30 mg/kg) compare to vehicle control over the 60 min test[1]. |
| Cell Assay | Rat, dog, rhesus monkey, and human plasma samples (3 mL, N=3) are incubated with 2 and 20 uM [14C] Rislenemdaz at 37°C for 30 min in a shaking water bath. Following incubation, standard ultracentrifugation methodology is used to determine the percentage of drug unbind[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Four groups of 24 rats (12/sex) are given single doses of vehicle (0.5% methylcellulose [MC] and 0.02% sodium lauryl sulfate [SLS] in deionized water) or Rislenemdaz at 10, 30 or 100 mg/kg by oral gavage at a dose volume of 10 mL/kg. Three additional groups of rats (four males and three females per group) are orally dosed in the same manner with Rislenemdaz, and 24h serial blood samples are obtained and analyzed for Rislenemdaz plasma concentrations and evaluated for systemic exposure. Young, adult, male rats are randomly assigned across the treatment groups and are administered vehicle (0.5% MC/0.02% SLS), the reference compound desipramine (20 mg/kg; a tricyclic antidepressant) dissolving in sterile water, or Rislenemdaz (0.1, 0.3, 1, 3, 10, and 30 mg/kg) suspending in 0.5% MC/0.02% SLS, twice on Day 1 (after habituation; ~24 h prior to test, and prior to dark cycle) and once on Day 2 (30 min pretest for desipramine and 45 min pretest for Rislenemdaz and vehicle)[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 527.4±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C19H23FN4O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 358.410 |
| Flash Point | 272.7±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 358.180511 |
| LogP | 2.73 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.584 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |