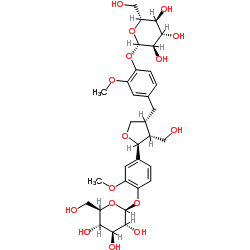
112747-98-5
| Name | 4-[(2S,3R,4R)-4-[4-(β-D-Glucopyranosyloxy)-3-methoxybenzyl]-3-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2-furanyl]-2-methoxyphenyl β-D-glucopyranoside |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
β-D-Glucopyranoside, 4-[(2S,3R,4R)-4-[[4-(β-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-3-methoxyphenyl]methyl]tetrahydro-3-(hydroxymethyl)-2-furanyl]-2-methoxyphenyl
4-[(2S,3R,4R)-4-[4-(β-D-Glucopyranosyloxy)-3-methoxybenzyl]-3-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2-furanyl]-2-methoxyphenyl β-D-glucopyranoside |
| Description | Clemastanin B, a lignin, has potent anti-influenza activities by inhibiting the virus multiplication, prophylaxsis and blocking the virus attachment. Clemastanin B targets viral endocytosis, uncoating or ribonucleoprotein (RNP) export from the nucleus. Clemastanin B has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Clemastanin B inhibits different subtypes of human (H1N1, including swine-origin H1N1; H3N2 and influenza B) and avian influenza viruses (H6N2, H7N3, H9N2) at different magnitudes of activity (IC50 0.087-0.72 mg/ml) while this compound was inactive against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), adenovirus 3 (ADV3), parainfluenza virus 3 (PIV3), enterovirus 71 (EV71) and human rhinovirus (HRV)[1]. Clemastanin B (0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.4 mg/ml; for 8 hours) treatment results in nucleoprotein (NP) distribution in the nuclei in MDCK cells[1]. Clemastanin B (48-72 h) after virus incubation (MOI, 0.01; for 2 h) causes a pronounced titer reduction of progeny virus in MDCK cells[1]. Clemastanin B (pre-incubated for 2 h) has no protective effect on MDCK cell lines with influenza virus[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 922.6±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C32H44O16 |
| Molecular Weight | 684.682 |
| Flash Point | 511.8±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 684.262939 |
| LogP | -2.82 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.630 |