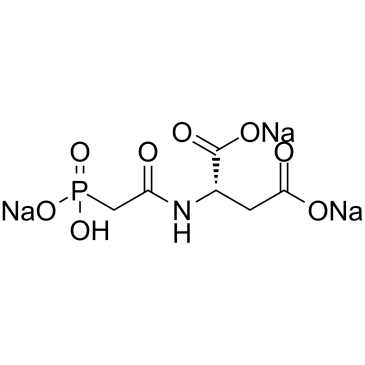
70962-66-2
| Name | Sparfosic acid trisodium |
|---|
| Description | Sparfosic acid trisodium, is a potent inhibitor of aspartate transcarbamoyl transferase, with anti-tumor and antimetabolite activity. Aspartate transcarbamoyl transferase catalyzes the second step of de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Sparfosic acid (PALA) treatment causes apoptosis in the resistant Br1 cells[1]. Sparfosic acid (PALA, 300 µM) shows progressive accumulation of cells in S phase and activation of an apoptotic pathway leading to cell death[1]. Cell Cycle Analysis[1] Cell Line: Br-l and L-2 cell lines established from metastasis in nude mouse injected with the human tumor cell line MDA-MB-435. Concentration: 300 µM. Incubation Time: 12, 24 and 48 h. Result: Cells were predominantly in S phase in both the cell lines, although slightly higher proportion of cells in S phase were noted in L-2 than Brl-3prl cells. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Line: Br-l and L-2 cell lines. Concentration: 300 µM. Incubation Time: 4, 10 and 24 h. Result: There was moderate difference in the level of phosphorylated Rb proteins seen in the two cell types. Marked increase in the amount of cyclin A protein was detected in the L-2 cells undergoing apoptosis with the highest level detected at 10 h post-drug treatment. In contrast, there was no increase in the level of cyclin A seen in the Brl-3prl cells. Cyclin E protein was found elevated in the L-2 cells and Brl-3prl cells compared to their respective controls. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C6H7NNa3O8P |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 321.06 |