565183-24-6
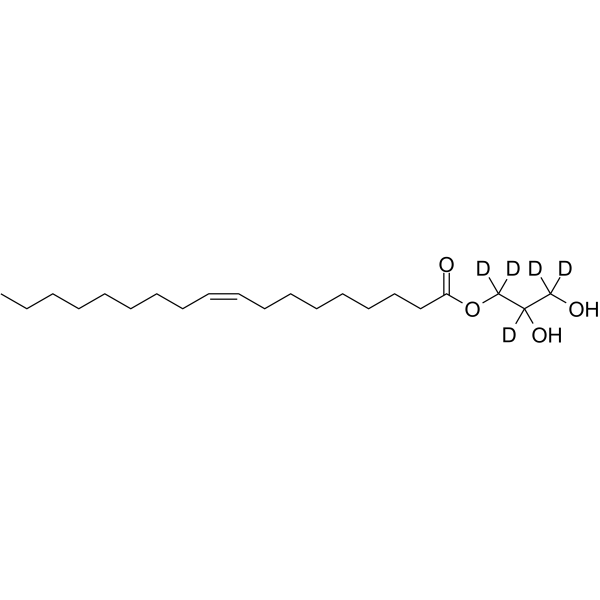
| Name | (1,1,2,3,3-pentadeuterio-2,3-dihydroxypropyl) (Z)-octadec-9-enoate |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
1-GLYCERYL OLEATE
Oleic monoglyceride Rylo MG 19-d5 1-monooleoyl-rac-glycerol 2,3-Dihydroxypropyl (9Z)-octadec-9-enoate a-Monoolein 1-Monooleoylglycerol 1-Monoolein-d5 Danisco MO 90 Glycerin 1-monooleate Glycerol 1-Oleate-d5 Monoolein (VAN) Glyceryl Monooleate (VAN) 2,3-Dihydroxypropyl Oleate-d5 Oleic acid glycerol monoester rac 1-Oleoyl Glycerol-d5 Glycerol |A-cis-9-Octadecenate-d5 dl-α-Monoolein Glycerol α-monooleate UNII:D3AEF6S35P 1-O-Oleyl-rac-glycerol 1-oleoyl glycerol Danisco MO 90-d5 1-OLEOYLGLYCEROL α-Monoolein rac-1-Monooleoylglycerol Glyceryl Monooleate-d5 Monoolein OLEOYL GLYCEROL 1-Mono(cis-9-octacenoyl)glycerol rac-1-Monooleoylglycerol-d5 2,3-Dihydroxypropyl (9Z)-9-octadecenoate Aldo HMO rac-1-Monoolein-d5 2,3-Dihydroxypropyl oleate rac 1-Oleoyl Glycerol-d5 |
| Description | Monoolein-d5 is the deuterium labeled Monoolein. Monoolein is an endogenous metabolite. |
|---|---|
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 483.3±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C21H35D5O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 361.57 |
| Flash Point | 155.4±19.4 °C |
| Exact Mass | 356.292664 |
| PSA | 66.76000 |
| LogP | 6.71 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.479 |