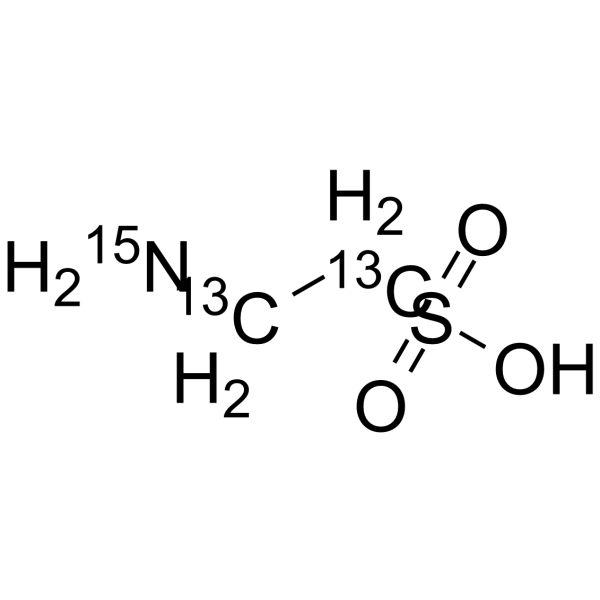2483830-42-6
| Name | Taurine-13C2,15N |
|---|
| Description | Taurine-13C2,15N (2-Aminoethanesulfonic acid-13C2,15N) is the 13C- and 15N- labeled Taurine. Taurine, a sulphur-containing amino acid and an organic osmolyte involved in cell volume regulation, provides a substrate for the formation of bile salts, and plays a role in the modulation of intracellular free calcium concentration. Taurine has the ability to activate autophagy in adipocytes[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
[2]. Ripps H, Shen W. Review: taurine: a "very essential" amino acid. Mol Vis. 2012;18:2673-2686. |
| Molecular Formula | 13C2H715NO3S |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 128.13 |