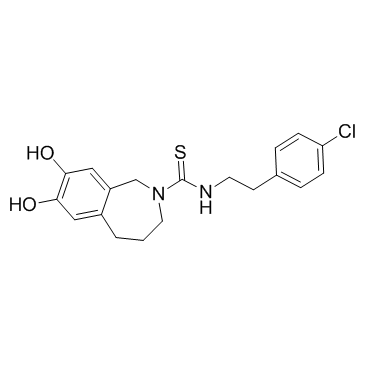
138977-28-3
| Name | capsazepine |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
N-[2-(4-Chlorophenyl)ethyl]-1,3,4,5-tetrahydro-7,8-dihydroxy-2H-2-benzazepine-2-carbothioamide
MFCD00153778 N-[2-(4-chlorophenyl)ethyl]-7,8-dihydroxy-1,3,4,5-tetrahydro-2-benzazepine-2-carbothioamide Capsazepine N-[2-(4-Chlorophenyl)ethyl]-7,8-dihydroxy-1,3,4,5-tetrahydro-2H-2-benzazepine-2-carbothioamide |
| Description | Capsazepine is a synthetic analogue of the sensory neurone excitotoxin, and an antagonist of TRPV1 receptor with an IC50 of 562 nM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
TRPV1 receptor[1] |
| In Vitro | Capsazepine (50 μM) optimally enhances the upregulation of (death receptors) DRs without affecting cell viability HCT116 cells. Capsazepine (30-50 μM) induces ROS generation and ROS mediate Capsazepine-induced DR5 upregulation in HCT116 cells[1]. Capsazepine (1-100 μM, 45 min preincubation) inhibits the evoked CGRP-LI release. Capsazepine (3-100 μM) prevents low pH- and capsaicin-induced CGRP-LI release from rat soleus muscle at concentrations which do not affect the release evoked by KCl. Capsazepine (3-100 μM, without 10 μM) produces a nonspecific inhibitory effect on CGRP-LI release from peripheral endings of the capsaicin-sensitive primary afferent neurone[2]. |
| In Vivo | Capsazepine (15 mg/kg, s.c.) prevents the increase in respiratory system resistance and decreases the increase in tissue damping during endotoxemia. Capsazepine attenuates lung injury evidenced by reduction on collapsed area of the lung parenchyma induced by LPS[3]. |
| Cell Assay | To assay intracellular ROS, HCT116 cells are preincubated with 20 μM dichlorofluorescein diacetate (DCF DA) for 15 min at 37°C and then treated with Capsazepine. After 1 h of incubation, the increase in fluorescence resulting from the oxidation of DCF DA to DCF is measured by flow cytometry. The mean fluorescence intensity at 530 nm is calculated for at least 10,000 cells at a flow rate of 250-300 cells/s. |
| Animal Admin | To verify the role of TRPV1 on lung mechanics during LPS-induced ALI, the animals (n = 10 per group) are pre-treated with vehicle or Capsazepine (15 mg/kg; s.c.), then receive saline or LPS (5 mg/kg, i.p.) after 10 min. Thus, the mice are randomly divided into four groups with 10 mice in each group: (i) control (vehicle + saline), (ii) Capsazepine + saline, (iii) vehicle + LPS and (iv) Capsazepine + LPS. After a 24-hr treatment with saline or LPS, the mice are anaesthetized and paralysed with pancuronium bromide and lung mechanics function is evaluated. Afterwards, the lungs are removed for histology. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 581.1±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 155-157°C |
| Molecular Formula | C19H21ClN2O2S |
| Molecular Weight | 376.900 |
| Flash Point | 305.3±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 376.101227 |
| PSA | 87.82000 |
| LogP | 3.50 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.672 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | methanol: soluble |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Phrases | R20/21/22 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | 2811 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(a) |