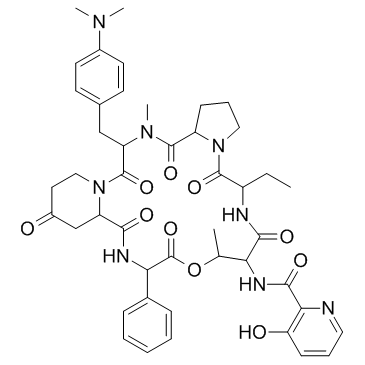
3131-03-1
| Name | pristinamycin IA |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Antibiotic PA 114B
Mikamycin B Ostreogrycin B PA 114B Pristinamycin IA Antibiotic PA 114 B1 Vernamycin BA Mikamycin IA Streptogramin B |
| Description | Pristinamycin IA is a cyclo-peptidic macrolactone antibiotic belonging to the streptogramin family, a substrate for the P-glycoprotein.In vitro: Pristinamycin IA specifically inhibits the efflux of the P-glycoprotein substrate [3H]vinblastine, thus increasing the cellular accumulation of the drug. Pristinamycin IA also reduces by 70% the basolateral to apical secretion of [3H]vinblastine across Caco-2 cell monolayers. The cellular accumulation of [14C]pristinamycin IA is very low and is increased by P-glycoprotein inhibitors (verapamil, chlorpromazine and reserpine). The basolateral to apical transport of [14C]pristinamycin IA is 100-fold higher than apical to basolateral passage. [1] |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.38g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 1202.1ºC at 760mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C45H54N8O10 |
| Molecular Weight | 866.95800 |
| Flash Point | 680.8ºC |
| Exact Mass | 866.39600 |
| PSA | 227.96000 |
| LogP | 2.13220 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| RIDADR | UN 3172 |
|---|---|
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |