22033-87-0
| Name | cholest-4-en-3-one oxime |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Cholest-4-en-3-on-oxim
3-oxyimino-cholest-4-ene olesoxime TRO 19622 |
| Description | Olesoxime (TRO 19622) is a mitochondrial-targeted neuroprotective compound with mean EC50 value for increasing cell survival is 3.2±0.2 µM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Mitochondrial[1] |
| In Vitro | Exposure to Olesoxime (TRO 19622) (ranging from 0.1 to 10 µM) at 1 h after plating significantly protects primary embryonic rat spinal MNs (that had been cultured for 3 days without brain-derived, ciliary and glia-derived neurotrophic factors) from cell death. At a concentration of 10 µM, Olesoxime (TRO 19622) maintains survival of 74±10% of the neurons supported by a combination of neurotrophic factors (brain-derived, ciliary and glia-derived neurotrophic factors). The mean EC50 in this assay is 3.2±0.2 µM. In addition to preserving MN cell bodies, Olesoxime (TRO 19622) also promotes the outgrowth of neurites. At a concentration of 1 µM, which increases cell survival by only 38%, Olesoxime (TRO 19622) increases overall neurite outgrowth per cell by 54%[1]. Olesoxime (TRO 19622) belongs to a new family of cholesterol-oximes identified for its survival-promoting activity on purified motor neurons deprived of neurotrophic factors. Olesoxime (TRO 19622) targets proteins of the outer mitochondrial membrane, concentrates at the mitochondria and prevents permeability transition pore opening mediated by, among other things, oxidative stress[2]. |
| In Vivo | Daily administration of Olesoxime (TRO 19622) (3 or 30 mg/kg sc) to adult mice for more than 2 months is well tolerated without toxicity or adverse effects[1]. When animals are treated orally for 5 days following the lesion, Olesoxime (TRO 19622) increases motor neuron cell body survival in a dose-dependent manner with significant rescue at the highest dose of 100 mg/kg. At this dose, motor neuron survival is 29 ±2% (n=18) corresponding to a 42% increase in survival compared with vehicle-treated animals[3]. Paclitaxel-treated rats that receive prophylactic treatment with 3 mg/kg/d or 30 mg/kg/d Olesoxime (TRO 19622) have 239±17.6 and 247±14.4 IENFs per cm, respectively. For both doses, the decreases are significantly less than the 46% decrease seen in the Paclitaxel-treated rats administered vehicle. However, both doses produce decreases (25% and 22%) that are significantly different relative to the naïve control group[4]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[3] Eight-week-old C57bl/6 RJ mice are anesthetized using 60 mg/kg i.p. ketamine chlorohydrate. To reduce the risk of gender-related differences in response to Olesoxime (TRO 19622), only female mice are used. The right sciatic nerve is surgically exposed at mid-thigh level, and it is crushed 5 mm proximal to the trifurcation of the sciatic nerve. The nerve is crushed twice for 30 s with hemostatic forceps (width, 1.5 mm) with a 90° rotation between each crush. Sciatic nerve degeneration/regeneration is assessed over 6 weeks by measurement of the compound muscular action potential (CMAP) and histological studies of the damaged area of the sciatic nerve. Olesoxime (TRO 19622) is given subcutaneously at 0.3, 3, and 30 mg/kg. Treatments started the day of the crush injury, and they continued daily for 6 weeks. In total, 15 animals per group are used in the study. Electromyography is performed once a week for 6 weeks using a Neuromatic 2000M electromyograph. Mice are anesthetized using 100 mg/kg i.p. ketamine chlorohydrate. CMAP is measured in the gastrocnemius muscle after a single 0.2-ms stimulation of the sciatic nerve at supramaximal intensity (12.8 mA). The amplitude (millivolts) and the latency (milliseconds) of the action potential are measured. Rats[4] Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats (200-300 g) are used. Olesoxime (TRO 19622) or the vehicle is administered via oral gavage in a volume of 5 mL/kg. The TRO19622doses used here (3-100 mg/kg) are chosen based on prior reports of neuroprotective and analgesic activity. |
| References |
| Density | 1.1 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 510ºC at 760mmHg |
| Melting Point | 145-148ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C27H45NO |
| Molecular Weight | 399.65200 |
| Flash Point | 341ºC |
| Exact Mass | 399.35000 |
| PSA | 32.59000 |
| LogP | 7.85800 |
| Vapour Pressure | 1.56E-12mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.583 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|
|
~89% 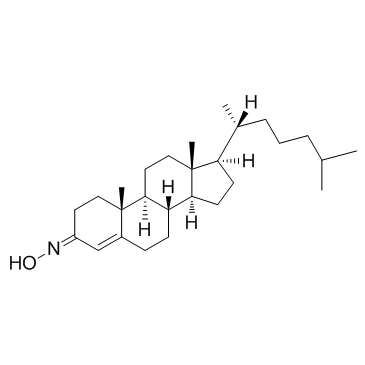
22033-87-0 |
| Literature: Hutchins, Robert O.; Rao, Samala J.; Adams, Jeffrey; Hutchins, Marygail K. Journal of Organic Chemistry, 1998 , vol. 63, # 22 p. 8077 - 8080 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 2 | |