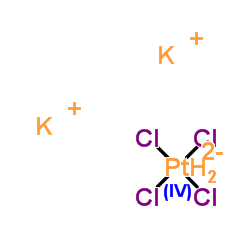
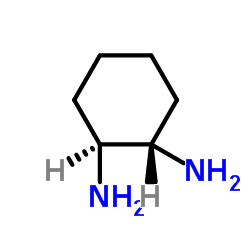
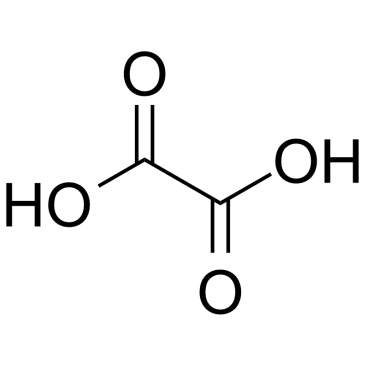
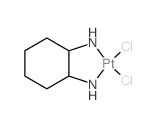
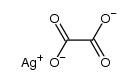
61825-94-3
| Name | oxaliplatin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Dacplat
Oxaliplatin MFCD00866327 platinum, [ethanedioato(2-)-κO,κO]-, compd. with (1R,2R)-1,2-cyclohexanediamine (1:1) Platinum(2+) ethanedioate - (1R,2R)-1,2-cyclohexanediamine (1:1) Platinum(2+) ethanedioate (1R,2R)-1,2-cyclohexanediamine (1:1) [Ethanedioato(2-)-κO,O]platinum - (1R,2R)-cyclohexane-1,2-diamine (1:1) Platinum(2+) ethanedioate (1R,2R)-1,2-cyclohexanediamine (1:1:1) Elocatin |
| Description | Oxaliplatin is a DNA synthesis inhibitor. It causes DNA crosslinking damage, prevents DNA replication and transcription and causes cell death. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Oxaliplatin acts through the formation of DNA-adducts. Oxaliplatin induces primary and secondary DNA lesions leading to cell apoptosis[1]. Oxaliplatin inhibits human melanoma cell lines C32 and G361 with IC50 values of 0.98 mM and 0.14 mM, respectively[2]. Oxaliplatin potently inhibits bladder carcinoma cell lines RT4 and TCCSUP, ovarian carcinoma cell line A2780, colon carcinoma cell line HT-29, glioblastoma cell lines U-373MG and U-87MG, and melanoma cell lines SK-MEL-2 and HT-144 with IC50 of 11 μM, 15 μM, 0.17 μM, 0.97 μM, 2.95 μM, 17.6 μM, 30.9 μM and 7.85 μM, respectively[3]. |
| In Vivo | Oxaliplatin (10 mg/kg, i.p.) significantly reduces tumor volume and apoptotic index in the nude mice bearing hepatocellular HCCLM3 tumors[4]. Oxaliplatin (5 mg/kg, i.v.) is effective on T-leukemia-lymphoma L40 AKR with T/C of 1.77. Oxaliplatin is efficient on intracerebrally grafted L1210 leukemia, MA 16-C xenografts, B16 melanoma xenografts, Lewis lung xenografts and C26 colon carcinoma xenografts[5]. Oxaliplatin induces impairment of retrograde neuronal transport in mice[6]. |
| Cell Assay | Typically, cells are plated into 96-well plates on day 0 and exposed to Oxaliplatin on day 1; the sulforhodamine-B assay is carried out 48 h after Oxaliplatin exposure. The plates are incubated at 37°C in 5% CO2 and 100% relative humidity at all times except when adding Oxaliplatin and during the final assay period. The initial number of cells plated for the assay ranged from 2-20×103 cells/50/nL/well. The numbers of cells for plating and the drug exposure time are based on pilot studies using the criteria that (a) the cells in control wells are still in the log phase of growth on the day of the assay; (b) the maximum absorbance for the untreated controls on the day of the assay is in the range of 1.0 to 1.5; and (c) cells go through > 2 doublings during the drug exposure. Eight wells are used per concentration. The plates are read at 570 and/or 540 nm using a Biotek Instruments model EL309 microplate reader interfaced with an IBM PC-compatible computer. |
| Animal Admin | HCC tumor models produced by HCCLM3 are established in nude mice by subcutaneous injection of 5×105 HCCLM3 cells in 0.2 mL of serum-free culture medium into the left upper flank region. Three days later, the mice are randomLy assigned to receive one of the following three treatments: i) a weekly intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of distilled water (control group, n=8); ii) a weekly i.p. injection of oxaliplatin at 5 mg/kg (low dose group, n=7); or iii) a weekly i.p. injection of oxaliplatin at 10 mg/kg (high dose group, n=7). Tumor growth is monitored by measuring two bisecting diameters of each tumor with a caliper every 5 days. The tumor volume is calculated using the formula (V=a×b2/2), with a as the larger diameter and b as the smaller diameter. Mice are euthanized by day 32 after oxaliplatin administration. Tumors of each group are completely removed, weighed, photographed, and fixed in 10% formalin/PBS or stored in liquid nitrogen for histological examination. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 193.6ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C8H12N2O4Pt |
| Molecular Weight | 395.28 |
| PSA | 104.64000 |
| LogP | 0.61450 |
| Appearance | solid |
| Storage condition | Store at +4°C |
| Stability | Stable. Store cool. Incompatible with oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | Slightly soluble in water, very slightly soluble in methanol, practically insoluble in anhydrous ethanol. | Soluble in water with heating and/or sonication |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H317-H319-H335-H351 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38;R40;R42/43 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | TP2275850 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| HS Code | 28439000 |
|
~20% 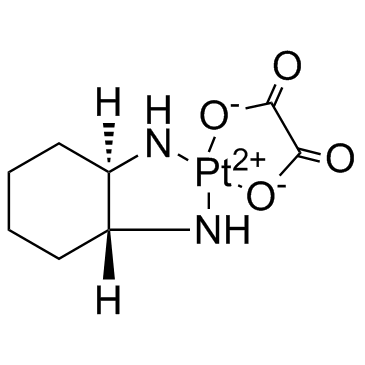
61825-94-3 |
| Literature: US2008/207935 A1, ; Page/Page column 7 ; |
|
~61% 
61825-94-3 |
| Literature: WO2007/140804 A1, ; Page/Page column 14-16 ; |
|
~40% 
61825-94-3 |
| Literature: Inorganica Chimica Acta, , vol. 401, p. 64 - 69 |
|
~39% 
61825-94-3 |
| Literature: US2008/207935 A1, ; Page/Page column 7 ; |
|
~49% 
61825-94-3 |
| Literature: WO2007/85957 A1, ; Page/Page column 13-16 ; |
|
~% 
61825-94-3 |
| Literature: Inorganic Chemistry, , vol. 27, p. 4106 - 4113 |
| Precursor 6 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |