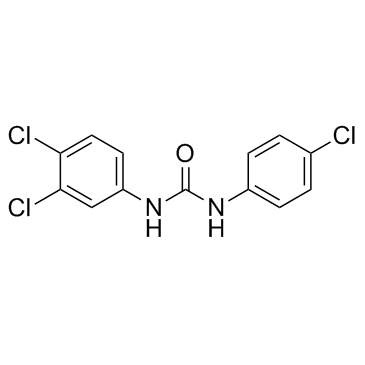
101-20-2
| Name | triclocarban |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
3,4,4'-Trichlorocarbanilide
N-(4-Chlorophenyl)-N'-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)carbamimidic acid 3,4,4′-Trichlorocarbanilide 3,4,4'-trichlorodiphenylurea cusiter MFCD00013254 Triclocarban Nobacter genoface GR DMVMR CG DG Procutene TCC CUTISAN N-(4-Chlorophenyl)-N-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-Urea EINECS 202-924-1 1-(4-Chlorophenyl)-3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)urea 3,4,4-Trichlorocarbanilide N-(4-Chlorophenyl)-N'-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)urea |
| Description | Triclocarban is an antimicrobial agent used in personal cleaning products. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Bacterial[1] |
| In Vitro | Triclocarban at 300 nM potentiates the cytotoxicity of 300 µM H2O2 in rat thymocytes. 300 nM triclocarban itself does not increase the population of death cells, it facilitates the process of cell death induced by H2O2, resulting in further increase in the population of dead cells[1]. Triclocarban exertes estrogenic activities by inducing luciferase activities in an ER reporter gene assay, promoting the proliferation of the MCF-7 cells, up-regulating the expression of pS2 and down-regulating ERα expression at both the mRNA and protein levels in the MCF-7 cells[2]. |
| In Vivo | Triclocarban is absorbed significantly from soap used during showering in human subjects and that its Cmax in their whole blood ranges from 23 nM to 530 nM[1]. Gestational triclocarban exposure does not affect the ability of dams to carry offspring to term but triclocarban exposure during lactation has adverse consequences on the survival of offspring[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats: Sprague Dawley rats are provided control, 0.2% weight/weight (w/w), or 0.5% w/w triclocarban -supplemented chow through a series of 3 experiments that limited exposure to critical growth periods: gestation, gestation and lactation, or lactation only (cross-fostering) to determine the susceptible windows of exposure for developmental consequences[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 475.3±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 254-256 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C13H9Cl3N2O |
| Molecular Weight | 315.582 |
| Flash Point | 241.2±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 313.978058 |
| PSA | 41.13000 |
| LogP | 5.66 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.630 |
| Storage condition | Refrigerator |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents strong bases. |
| Water Solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL at 26 ºC |
| Symbol |

GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H410 |
| Precautionary Statements | P273-P501 |
| Hazard Codes | N |
| Risk Phrases | R50/53 |
| Safety Phrases | S60-S61 |
| RIDADR | UN 3077 9/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | FE1250000 |
| Hazard Class | 9.0 |
| HS Code | 2924299090 |
|
~% 
101-20-2 |
| Literature: Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 79, p. 1236,1242 Journal of Organic Chemistry, , vol. 24, p. 1676 |
|
~% 
101-20-2 |
| Literature: US2818390 , ; US2846398 , ; |
|
~% 
101-20-2 |
| Literature: Indian Journal of Chemistry, Section B: Organic Chemistry Including Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 37, # 10 p. 1066 - 1068 |
| HS Code | 2924299090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924299090. other cyclic amides (including cyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |