100981-43-9
| Name | N-(4-bromophenyl)sulfonyl-N'-[2-[[2-(diaminomethylideneamino)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]methylsulfanyl]ethyl]methanimidamide |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
4-Bromo-N-[(E)-({2-[({2-[(diaminomethylene)amino]-1,3-thiazol-4-yl}methyl)sulfanyl]ethyl}imino)methyl]benzenesulfonamide
Ebrotidina [Spanish] Ebrotidina 4-bromo-N-{(E)-[(2-{[(2-carbamimidamido-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)methyl]sulfanyl}ethyl)amino]methylidene}benzenesulfonamide Ebrotidine Benzenesulfonamide,N-(((2-(((2-((aminoiminomethyl)amino)-4-thiazolyl)methyl)thio)ethyl)amino)methylene)-4-bromo-,(E) n-p-bromobenzenesulfonyl-n'-[2-[[[2-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]-4-thiazolyl]methyl]thio]ethyl]formamidine Ebrotidinum [Latin] Ebrotiding N-[[[2-[[[2-[(Aminoiminomethyl)amino]-4-thiazolyl]methyl]thio]ethyl]amino]methylene]-4-bromobenzenesulfonamide FI-3542 p-Bromo-N-[[[2-[[[2-[(diaminomethylene)amino]-4-thiazolyl]methyl]thio]ethyl]amino]methylene]benzenesulfonamide Ulsanic Ebrotidinum |
| Description | Ebrotidine(FI 3542) is a competitive H2-receptor antagonist (Ki= 127.5 nM) with a potent antisecretory activity and evidenced gastroprotection.IC50 Value: 127.5 nM (Ki)[1]; 0.21mg/kg (ED50, histamine- stimulated acid secretion) [2]Target: H2 receptorin vitro: Ebrotidine displaced 3H-thiotidine specific binding to histamine H2-receptors (Ki: 127.5 nmol/l), showing a higher affinity (p < 0.05) than ranitidine (Ki: 190.0 nmol/l) and cimetidine (Ki: 246.1 nmol/l) [1]. in vivo: Following intravenous administration to rats, ebrotidine inhibited histamine- and pentagastrin-stimulated acid secretion in a dose-dependent manner, ED50 being 0.21 and 0.44 mg/kg, respectively [2]. The mean number of gastric erosions seen at endoscopy after treatment with ebrotidine plus ASA (2.0 +/- 0.3) was significantly lower than that after placebo plus ASA (3.7 +/- 0.2). This reduction in lesion core by ebrotidine was accompanied by a significant increase in gastric blood flow (by 15% in corpus and 26% in antrum), by a rise in transmucosal potential difference (by 12%), and by a decrease of mucosal microbleeding [3]. Results of macroscopic assessment revealed that ebrotidine at doses of 50mg and higher/kg body weight effectively prevented mucosal injury, and that the maximal protective effect was achieved by 1h. Physicochemical analysis established that ebrotidine evoked 30% increase in mucus gel dimension, and showed 20% increase in phospholipids, and the content of sulfo- (18%) and sialomucins (21%) [4]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 672.3±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C14H17BrN6O2S3 |
| Molecular Weight | 477.423 |
| Flash Point | 360.4±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 475.975830 |
| PSA | 195.24000 |
| LogP | 3.37 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.740 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
|---|
|
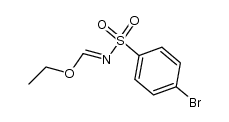
~57% 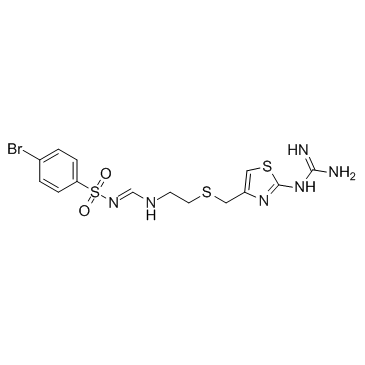
100981-43-9 |
| Literature: Anglada; Marquez; Sacristan; Ortiz European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 1988 , vol. 23, # 1 p. 97 - 100 |
|
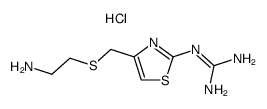
~60% 
100981-43-9 |
| Literature: Rozman; Galceran; Anglada; Albet Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 1994 , vol. 83, # 2 p. 252 - 254 |
|
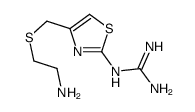
~% 
100981-43-9 |
| Literature: European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 23, # 1 p. 97 - 100 |
|
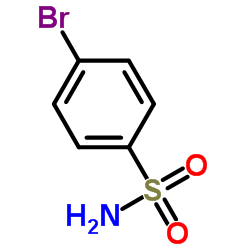
~% 
100981-43-9 |
| Literature: Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, , vol. 83, # 2 p. 252 - 254 |
| Precursor 5 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
|---|