640-79-9
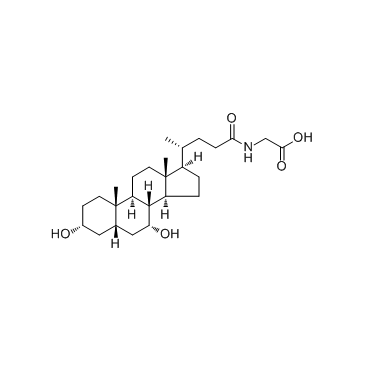
| Name | glycochenodeoxycholic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Chenodeoxycholylglycine
[3H]-Glycylchenodeoxycholic acid [14C]-Glycylchenodeoxycholic acid 2-[[(4R)-4-[(3R,5S,7R,8R,9S,10S,13R,14S,17R)-3,7-dihydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]pentanoyl]amino]acetic acid Glycine chenodeoxycholate Chenodeoxyglycocholic acid Chenodeoxycholic acid glycine conjugate Glycochenodeoxycholate Chenodeoxyglycocholate |
| Description | Glycochenodeoxycholic acid is a bile salt formed in the liver from chenodeoxycholate and glycine; used to induce hepatocyte apoptosis in research. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Chenodeoxycholate is toxic to hepatocytes, and accumulation of chenodeoxycholate in the liver during cholestasis may potentiate hepatocellular injury. At a concentration of 250μM, glycochenodeoxycholate is more toxic than either chenodeoxycholate or taurochenodeoxycholate. Glycochenodeoxycholate cytotoxicity may result from ATP depletion followed by a subsequent rise in Ca2+. The rise in Ca2+ leads to an increase in calcium-dependent degradative proteolysis and, ultimately, cell death[1]. 4 h exposure of 50 μM GCDC induces apoptosis in 42% of hepatocytes. Intracellular PKC activity decreased to 44% of controls 2 h after exposure of hepatocytes to GCDC. GCDC-induced apoptosis is associated with decreases in total cellular PKC activity, which appear to be dependent on intracellular calpain-like protease activity[2]. |
| In Vivo | GCDCA induces ER-related calcium release within about ten seconds. Significant increases in activities of calpain and caspase-12 are observed after 15 h of GCDCA treatment. Bip and Chop mRNA expressions are increased with the treated GCDCA dose and incubation time. Cytochrome c release from mitochondria peaks in about 2 h of incubation[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats: The freshly isolated hepatocytes are preincubated for 2 h at a density of 1× 106 cells/mL in a mixture of William’s E medium supplement with 10% FBS. Isolated rat hepatocytes are incubated in William’s E medium with or without (used as a control) GCDCA (50, 100 and 300 μM), or TG (1, 2 and 5 μM) for 1-24 h[3]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C26H43NO5 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 449.62300 |
| Exact Mass | 449.31400 |
| PSA | 110.35000 |
| LogP | 4.43440 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |