863031-21-4
| Name | azilsartan medoxomil |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Azilsartan kamedoxomil
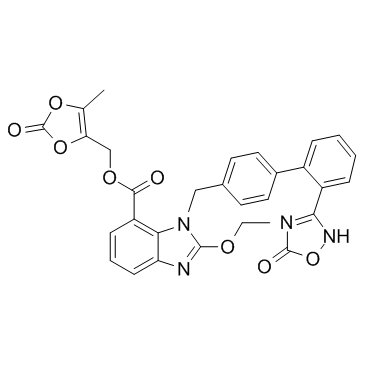
(5-methyl-2-oxo-1,3-dioxol-4-yl)methyl 2-ethoxy-3-[[4-[2-(5-oxo-2H-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)phenyl]phenyl]methyl]benzimidazole-4-carboxylate (5-methyl-2-oxo-1,3-dioxol-4-yl)methyl 2-ethoxy-1-((2'-(5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)biphenyl-4-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-7-carboxylate TAK 491 azilsartanum medoxomilum Azilsartan (5-Methyl-2-oxo-1,3-dioxol-4-yl)methyl 2-ethoxy-1-{[2'-(5-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)-4-biphenylyl]methyl}-1H-benzimidazole-7-carboxylate (5-methyl-2-oxo-1,3-dioxol-4-yl)methyl ester of 1-[[2'-(2,5-dihydro-5-oxo-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl]-2-ethoxy-1H-benzimidazole-7-carboxylic acid UNII-LL0G25K7I2 Azilsartan medoxomil Azilsartan (medoxomil) 1H-Benzimidazole-7-carboxylic acid, 1-[[2'-(2,5-dihydro-5-oxo-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl]-2-ethoxy-, (5-methyl-2-oxo-1,3-dioxol-4-yl)methyl ester Edarbi [14C]-Azilsartan medoxomil |
| Description | Azilsartan medoxomil(TAK 491) is an orally administered angiotensin II receptor type 1 antagonist with IC50 of 0.62 nM, which used in the treatment of adults with essential hypertension. IC50 Value: 0.62 nM [2]Target: AT1 receptorin vitro: In aortic endothelial cells, azilsartan inhibited cell proliferation at concentrations as low as 1 μmol/l, whereas valsartan showed little or no antiproliferative effects at concentrations below 10 μmol/l. Antiproliferative effects of azilsartan were also observed in cells lacking AT1 receptors[1].in vivo: Oral administration of 0.1-3 mg/kg olmesartan medoxomil reduced blood pressure; however, only the two highest doses significantly reduced blood pressure 24h after dosing. ED(25) values were 0.41 and 1.3 mg/kg for azilsartan medoxomil and olmesartan medoxomil, respectively [2]. Over a longer treatment period of 24 weeks, azilsartan medoxomil showed sustained BP-lowering efficacy, with the reduction in 24-hour mean SBP at week 24 significantly greater with azilsartan medoxomil 40 or 80 mg once daily than with valsartan 320 mg once daily. Mean reductions from baseline in mean clinic SBP and DBP as well as DBP by ABPM were also significantly greater with azilsartan medoxomil 40 or 80 mg once daily than with valsartan[3]. In 4 randomized controlled trials (3 published to date), azilsartan medoxomil/chlorthalidone 40 mg/12.5 mg and 40 mg/25 mg reduced blood pressure (BP) significantly more than comparators did, including an approximately 5-mm Hg greater BP reduction than olmesartan medoxomil/hydrochlorothiazide 40 mg/25 mg and azilsartan medoxomil/hydrochlorothiazide [4].Clinical trial: Effect of Azilsartan on Aldosterone in Post-menopausal Females . Phase not specified |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 748.0±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C30H24N4O8 |
| Molecular Weight | 568.534 |
| Flash Point | 406.2±35.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 568.159424 |
| PSA | 155.59000 |
| LogP | 5.73 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.680 |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |
| Precursor 6 | |
|---|---|
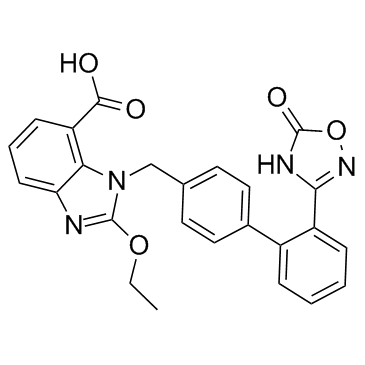
| DownStream 1 | |



![Methyl 1-((2'-cyano-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)methyl)-2-ethoxy-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-7-carboxylate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/354/139481-44-0.png)
![2-Ethoxy-1-[[2'-[(hydroxyamino)iminomethyl][1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl]-1H-benzimidazole-7-carboxylic acid methyl ester structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/472/147403-65-4.png)