215168-33-5
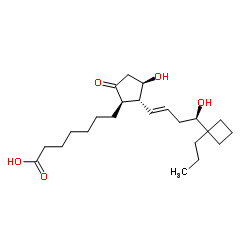
| Name | 7-{(2R)-3-Hydroxy-2-[(1E,4R)-4-hydroxy-4-(1-propylcyclobutyl)-1-b uten-1-yl]-5-oxocyclopentyl}heptanoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
7-{(1R,2R,3R)-3-Hydroxy-2-[(1E,4R)-4-hydroxy-4-(1-propylcyclobutyl)-1-buten-1-yl]-5-oxocyclopentyl}heptanoic acid
(11α,13E,16R)-11,16-Dihydroxy-9-oxo-17-propyl-17,20-cycloprost-13-en-1-oic acid |
| Description | (R)-Butaprost (free acid). Butaprost is a structural analog of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) with good selectivity for the EP2 receptor subtype. Butaprost is frequently used pharmacologically to define the expression profile of EP receptors in various human and animal tissues and cells. Gardiner caused serious confusion about the structure of butaprost in 1986 when he reported that the epimer of butaprost showing this selective activity was the C-16 (R)-epimer ( See reference 2 and notes). To increase the binding affinity of (R)-butaprost to prostaglandin receptors, we removed the methyl ester of (R)-butaprost and recreated the native C-1 carboxylic acid. Prostaglandin free acids typically bind their cognate receptors with 10 to 100-fold higher affinity than the corresponding ester derivatives. The pharmacology of (R)-butaprost has not been carefully studied, but it is generally considered to be the less active C-16 epimer. (Note: In the 1986 Gardiner paper in the British Journal of Pharmacology, butaprost appears on page 46 under the designation TR 4979. The structure drawn is incorrect because the authors use and refer to the more active C - The 16 epimer, which is actually 16(S). The structure on page 46 shows the structure as 16(R). It was not until the late 1990s that careful studies in the United States and Japan correctly determined the actual structure of C-16 The type is 16(S) in a compound called butaprost.) |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 565.7±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C23H38O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 394.545 |
| Flash Point | 310.0±26.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 394.271912 |
| PSA | 94.83000 |
| LogP | 3.04 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.558 |