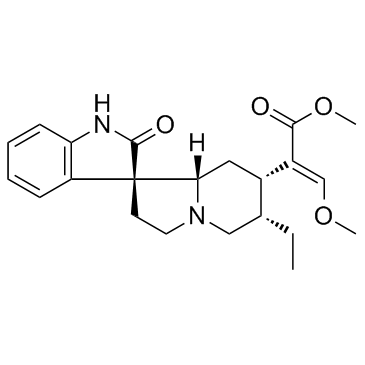
6877-32-3
| Name | Corynoxine |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Methyl (16E)-16-(methoxymethylene)-2-oxocorynoxan-17-oate |
| Description | Corynoxine is an enantiomer of Corynoxine B; induces autophagy in different neuronal cell lines, including N2a and SHSY-5Y cells.IC50 value:Tareget: Autophagy inducerIn vivo, Cory promotes the formation of autophagosomes in the fat bodies of Drosophila. By inducing autophagy, Cory promotes the clearance of wild-type and A53T α-syn in inducible PC12 cells. Interestingly, different from its enantiomer Cory B, Cory induces autophagy through the Akt/mTOR pathway as evidenced by the reduction in the levels of phospho-Akt, phospho-mTOR and phospho-p70 S6 Kinase [1]. Corynoxine significantly decreased locomotor activity after oral administration to mice [2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 560.8±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 166-168ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C22H28N2O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 384.469 |
| Flash Point | 293.0±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 384.204895 |
| PSA | 67.87000 |
| LogP | 3.31 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.596 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |