55721-11-4
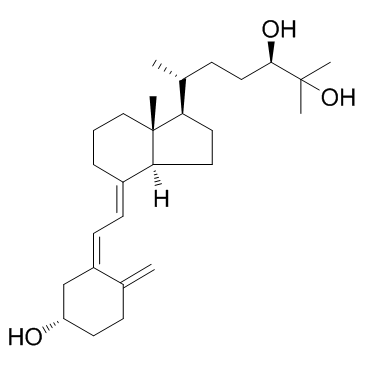
| Name | (24R)-24,25-dihydroxycalciol |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
k-dr
(3S,5Z,7E,14β,24R)-9,10-Secocholesta-5,7,10-triene-3,24,25-triol Secalciferol osteod |
| Description | Secalciferol is a metabolite of Vitamin D, a possibly anti-inflammatory steroid which is involved in bone ossification. IC50 value:Target: In addition, it is known that Secalciferol mediates calcium and phosphorus homeostasis. Also Secalciferol inhibits calcium channels in osteosarcoma cells via suppressing the effects of 1α, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and testosterone. Alternate studies indicate that Secalciferol can decrease the abundance of p53 and Pi-induced cytochrome c translocation. Furthermore, Secalciferol can increase cell proliferation in resting zone (RC) chondrocytes and inhibits matrix enzymes by possibly inhibiting the degradation of the matrix. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 571.1±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 63-65ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C27H44O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 416.637 |
| Flash Point | 241.5±20.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 416.329041 |
| PSA | 60.69000 |
| LogP | 5.85 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.547 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301 + H311-H330-H372 |
| Precautionary Statements | P260-P280-P284-P301 + P310-P310 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T+:Verytoxic; |
| Risk Phrases | R28 |
| Safety Phrases | S28-S36/37-S45 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 |
| RTECS | VS2895000 |