71261-64-8
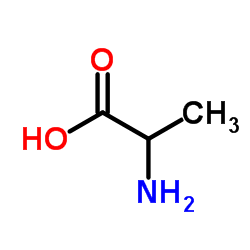
| Name | 2-azanylpropanoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
(R,S)-Alanine
(±)-Alanine DL-Alanine-15N DL-2-aminopropionic acid α-Aminopropanoic acid (15N)-dl-alanine 2-Aminopropanoic acid (15)N-alanine ZY1&VQ Alanine α-Aminopropionic acid d,l-alanine DL-15N-alanine UNII:1FU7983T0U α-Alanine MFCD00064409 2-Aminopropionic Acid DL-α-Aminopropionic acid H-DL-Ala-OH DL-2-Aminopropanoic acid DL-α-Alanine DL-Aminopropanoic acid Methyl glycine |
| Description | DL-Alanine-15N is the 15N labeled DL-Alanine[1]. DL-alanine, an amino acid, is the racemic compound of L- and D-alanine. DL-alanine is employed both as a reducing and a capping agent, used with silver nitrate aqueous solutions for the production of nanoparticles. DL-alanine can be used for the research of transition metals chelation, such as Cu(II), Zn(II), Cd(11). DL-alanine, a sweetener, is classed together with glycine, and sodium saccharin. DL-alanine plays a key role in the glucose-alanine cycle between tissues and liver[2][3][4][5][6][7]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
[5]. Tapper DN, et al. Taste stimuli: a behavioral categorization. Science. 1968 Aug 16161(3842):708-10. |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 212.9±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 289ºC (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C3H7NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 89.093 |
| Flash Point | 82.6±22.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 89.047676 |
| PSA | 63.32000 |
| LogP | -0.68 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.1±0.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.460 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|