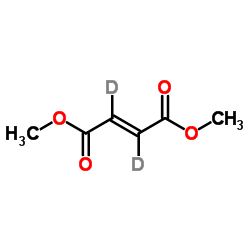
24461-32-3
| Name | (E)-2,3-dideuteriobut-2-enedioic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
(2E)-(H)-2-Butenedioic acid
(2E)-(H)But-2-enedioic acid 2,3-dideuterio-fumaric acid Fumaric acid-2,3-d2 2,3-2H-fumaric acid Maleic acid-2,3-d2 2,3-Dideuterio-fumarsaeure MFCD00144378 |
| Description | Fumaric acid-d2 is the deuterium labeled Fumaric acid[1]. Fumaric acid, associated with fumarase deficiency, is identified as an oncometabolite or an endogenous, cancer causing metabolite[2]. |
|---|---|
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 355.5±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 299-300ºC (subl.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C4H2D2O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 118.085 |
| Flash Point | 183.0±19.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 118.023514 |
| PSA | 74.60000 |
| LogP | -0.01 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.526 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Phrases | R41;R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
~90% 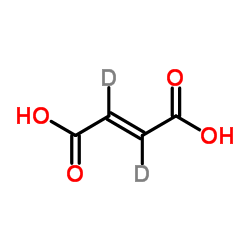
24461-32-3 |
| Literature: Journal of the Chemical Society, Perkin Transactions 1: Organic and Bio-Organic Chemistry (1972-1999), , # 10 p. 2387 - 2392 |
|
~89% 
24461-32-3 |
| Literature: Tetrahedron, , vol. 46, # 18 p. 6381 - 6398 |
|
~% 
24461-32-3 |
| Literature: European Journal of Organic Chemistry, , # 2 p. 387 - 401 |
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |