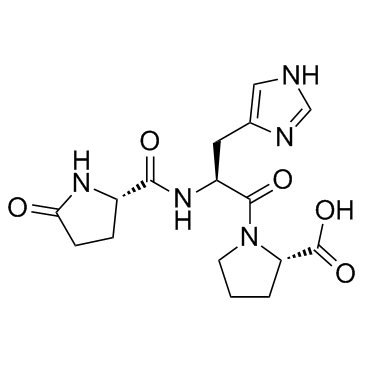
24769-58-2
| Name | trh |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
N-L-pyroglutamyl-glycine
L-Pyroglutamyl-L-histidyl-L-prolin pyroglutamylglicine pyro-L-Glu-L-His-L-Pro-OH pGlu-His-Pro-OH Glp-His-Pro-OH thyrotropin-releasing hormone-OH PGLU-GLY-OH pyroglutamylglycine N-L-Pyroglutamyl-glycin EpiderMal Dipeptide,EDP Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone (TRH), Free Acid |
| Description | Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone (TRH), Free Acid (TRH-OH) is a physiological metabolite of Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | TRH degradation products have been shown to be associated with a number of endocrine- and central nervous system-related biological functions. TRH (pGlu-His-Pro-NH2) can be enzymatically degraded in plasma and brain tissue to yield TRH-OH. TRH and hGHRH stimulate the release of [3H]GH into the culture medium to 435 and 464%, respectively, when compared to the control, but TRH-OH has no effect[1]. TRH-OH, produced after cleavage of the C-terminal amide group by a specific proline endopeptidase, is one of the most stable derivatives of TRH and is found at high levels in numerous brain regions. TRH-OH inhibits Na+ channel activity in mammalian septal neurons. In about 60% of the cells tested, TRH-OH at concentrations between 0.01 and 2.5 μM produces a dose-dependent reversible attenuation of Na+ currents. With 2 μM TRH-OH, peak Na+ current amplitude is reduced by 20-50%[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.64g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H21N5O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 363.37 |
| PSA | 49.33000 |
| LogP | 2.76740 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.741 |