65646-68-6
| Name | 4-hydroxyphenyl retinamide |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
4-Hydroxyphenyl retinamide
Fenretinide 4-HPR 15-[(4-Hydroxyphenyl)amino]retinal fenretinida fenretinidum MFCD00792674 |
| Description | Fenretinide is a synthetic retinoid deriverative, binding to the retinoic acid receptors (RAR) at concentrations necessary to induce cell death. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Fenretinide exerts not just acute but also long term antitumor activity in selected T-ALL cell lines. Fenretinide inhibits DES activity in CCRF-CEM leukemia cells in a dose and time dependent manner, leading to a concomitant increase of the endogenous cellular dhCer content. Fenretinide (3 μM)-induced dhCer accumulation in both CCRF-CEM and Jurkat cells[1]. Ceramide inhibition with fenretinide protects insulin signaling. Fenretinide prevents lipid-induced reductions in insulin-stimulated glucose uptake[2]. Fenretinide inhibits OVCAR-5 cell proliferation and viability at concentrations higher than 1 microM, with 70-90% growth inhibition at 10 microM. Fenretinide (1 microM) significantly inhibits OVCAR-5 invasion after 3 days preincubation. Endothelial cells treated with 1 microM 4-HPR fails to form tubes, but forms small cellular aggregates[4]. |
| In Vivo | Fenretinide (10 mg/kg, i.p.) selectively inhibits ceramide accumulation HFD-fed male C57Bl/6 mice. Fenretinide treatment improves glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity as determined by both glucose and insulin tolerance tests[2]. Addition of 25 mg/kg ketoconazole to Fenretinide in NOD/SCID mice increased 4-HPR plasma levels[3]. |
| Cell Assay | Standard XTT assay is used to determine cell viability. For fenretinide-only treatments, cells are plated in 96-well plates at 750,000 cells/mL and 100 μL/well. After 4 h, treatments are added on 50 μL/well obtaining a final density of 500,000 cells/mL and final volume of 150 μL/well. Four replicates are used per experimental condition. XTT reagent mixture is added 4 h before the end of selected treatment period and absorbance at 490 nm is determined per each well. A slightly modified protocol is used for analysis of the effect of myriocin (final concentration of 100 nM) or antioxidant on Fenretinide treatment. Briefly, cells are seeded on 60 mm culture dishes and myriocin or antioxidants added after 4 h. Fenretinide treatment is added 2 h later and cells are plated in quadruplicates in 96 well plates (150 μL/well). |
| Animal Admin | Male mice (C57Bl6) are fed a standard chow or a high-fat diet (HFD) from 5 to 17 weeks, at which point half of the HFD-fed mice begin receiving fenretinide in drinking water for 4 weeks. Fenretinide is dissolved in 100% ethanol and diluted in water to 10 μg/mL. Control treatment water receives an equal amount of ethanol (0.5%). FEN water is prepared in low-light conditions and administered in light-protective bottles. Water is replaced every 1-2 days, and no precipitation of FEN is noted at any time. Animal weights are recorded at the beginning and end of the treatment period. Following a 4-week FEN treatment, mice undergo intraperitoneal glucose and insulin tolerance tests. For both tests, mice are fasted for 6 h andreceive an injection of either glucose (1 g/kg of body weight) or insulin (0.75 units/kg of body weight). Blood glucose is determined at the times indicated by the Bayer Contour® glucose meter, and insulin is measured with the rat/mouse insulin ELISA kit. The insulin resistance index is assessed by using fasting blood glucose and insulin levels to compute the homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), where a higher number represents greater insulin resistance. |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 597.6±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 162-163°C |
| Molecular Formula | C26H33NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 391.546 |
| Flash Point | 315.2±27.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 391.251129 |
| PSA | 49.33000 |
| LogP | 7.41 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.607 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Stability | Light Sensitive - Protect from Light Exposure |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H302 + H312 + H332-H315-H319-H335-H360 |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P261-P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P308 + P313 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T: Toxic; |
| Risk Phrases | R60;R61;R20/21/22;R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S53-S26-S36/37/39-S45 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | VH6420000 |
|
~82% 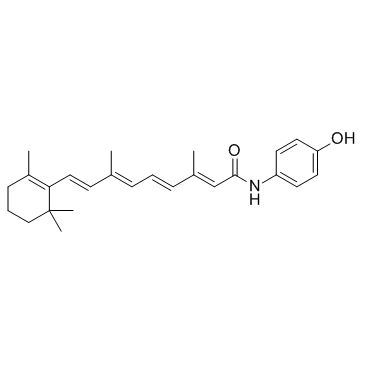
65646-68-6 |
| Literature: Sangmam, Charles; Winum, Jean-Yves; Lucas, Marc; Montero, Jean-Louis; Chavis, Claude Synthetic Communications, 1998 , vol. 28, # 16 p. 2945 - 2958 |
|
~% 
65646-68-6 |
| Literature: Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, , vol. 73, # 6 p. 745 - 751 |
|
~% 
65646-68-6 |
| Literature: Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters, , vol. 17, # 3 p. 836 - 840 |
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |


![[4-[[(2Z,4E,6E,8E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohexen-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoyl]amino]phenyl] 2,2-dimethylpropanoate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/492/75664-77-6.png)