84-80-0
| Name | phylloquinone |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
KONAKION
Rac-Phytonadione-D7 Phylloquinone-d3 VITAMIN K1 (PHYTONADIONE) Veda K1 2-Methyl-3-[(2E,7R,11R)-3,7,11,15-tetramethyl-2-hexadecen-1-yl]-1,4-naphthoquinone Kephton Antihemorrhagic vitamin 2-METHYL-3-PHYTYL-1,4-NAPHTHOQUINONE 2-methyl-3-[(2E,7R,11R)-3,7,11,15-tetramethylhexadec-2-en-1-yl]naphthalene-1,4-dione 2',3'-trans-Vitamin K1 AQUAMEPHYTON Combinal K1 Orakay 2-méthyl-3-[(2E,7R,11R)-3,7,11,15-tétraméthylhexadéc-2-én-1-yl]naphtalène-1,4-dione EINECS 201-564-2 Vitamin K1 Veta K1 [R-[R*,R*-(E)]]-2-Methyl-3-(3,7,11,15-tetramethyl-2-hexadecenyl)-1,4-naphthalenedione VITAMIN K1-[2H7] (PHYTONADIONE) Phyllochinonum Phytonadione, K1 VITAMIN K/PHYLLOQUINONE phytomenadione Kaywan 2-Methyl-3-[(2E,7R,11R)-3,7,11,15-tetramethylhexadec-2-en-1-yl]naphthalen-1,4-dion 2-Methyl-3-[(2E,7R,11R)-3,7,11,15-tetramethylhexadec-2-en-1-yl]-1,4-naphthoquinone 2-Methyl-3-((2E,7R,11R)-3,7,11,15-tetramethyl-2-hexadecenyl)-1,4-naphthalenedione Aqua mephyton vitamin K1 quinone Vitamin K1 (VAN) Kativ N K-Ject VITAMIN K<SUBSCRIPT>1</SUBSCRIPT> Synthex P 2',3'-t Phytylmenadione kativn Mono-kay MFCD00214063 PHYTONADIONE Kinadion Vitamin- K1 Phylloquinone (8CI) PHYTOMENADIONE, BP STANDARD |
| Description | Vitamin K1 a fat-soluble, naturally occurring vitamin required for blood coagulation and bone and vascular metabolism. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Phylloquinone (Vitamin K1) is a prenylated naphthoquinone that is synthesized exclusively by plants, green algae, and some species of cyanobacteria, where it serves as a vital electron carrier in photosystem I and as an electron acceptor for the formation of protein disulfide bonds. In humans and other vertebrates, phylloquinone plays the role of a vitamin (vitamin K1) that is required for blood coagulation and bone and vascular metabolism. Phylloquinone from green leafy vegetables and vegetable oil represents the major dietary source of vitamin K for humans[1]. Vitamin K1 treatment causes a significant antiproliferative effect and induces apoptosis in Caco-2, HT-29, and SW480 cell lines, with the involvement of the MAPK pathway. A concomitant and significant decrease in the polyamine biosynthesis occurr[2]. |
| In Vivo | Subjects who increase their dietary intake of vitamin K during the follow-up had a 51% reduced risk of incident diabetes compared with subjects who decrease or does not change the amount of phylloquinone intake[3]. Vitamin K supplementation reverses the high fat diet induced bone deterioration by modulating osteoblast and osteoclast activities and prevent bone loss in a high-fat diet-induced obese mice[4]. Application of vitamin K1 to the skin has been used for suppression of pigmentation and resolution of bruising. The effects produced by the topical vitamin K1 shows significant healing when compared with control group in parameters such as wound contraction, epithelialization period, hydroxyproline content and tensile strength[5]. |
| Cell Assay | Caco-2, HT-29, and SW480 cells are treated with increasing concentrations of vitamin K1 (10, 50, 100, and 200 μM) for 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h. MTT is added to each dish and incubated for 2 h at 37°C. At the end of the incubation period, the medium is removed. The plate is read at 570 nM[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats: For inducing full-thickness wound in rats, the excisional wound model is used. Five groups consisting of 8 rats each are used. Vitamin K cream (1% and 2%, w/w) is prepared in eucerin base and applied on the wound once a day until complete healing had occurred. Healing is defined by decreased wound margin (wound contraction), re-epithelialization, tensile strength and hydroxyproline content. Histopathological examination is also done[5]. Mice: Four-week-old C57BL/6J male mice are fed a 10% fat normal diet group or a 45% kcal high-fat diet group, with or without 200 mg/1000 g vitamin K1 (Normal diet + K1, high-fat diet + K1) and 200 mg/1000 g vitamin K2 (Normal diet + K2, high-fat diet + K2) for 12 weeks[4]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 546.4±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | −20 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C31H46O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 450.696 |
| Flash Point | 200.4±27.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 450.349792 |
| PSA | 34.14000 |
| LogP | 12.25 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.511 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | QJ5800000 |
| HS Code | 2936290090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 3 | |
| HS Code | 2936290090 |
|---|





![(E/Z)-[2-Methyl-4-(2'-tetrahydropyranyloxy)-2-butenyl]chlorid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/495/55453-94-6.png)
![Essigsaeure-[(E)-2-methyl-4-(3',4',5',6'-tetrahydro-2'H-pyran-2'-yl)oxy-2-butenyl]ester structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/064/66432-56-2.png)
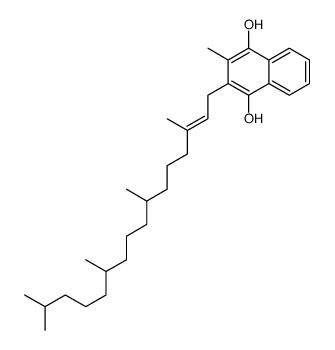
![[R-[R*,R*-(E)]]-2-methyl-3-(3,7,11,15-tetramethylhexadec-2-enyl)naphthalene-1,4-diol structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/364/572-96-3.png)