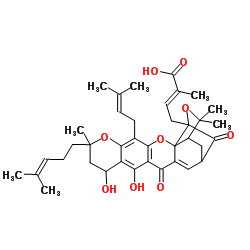
93772-31-7
| Name | Neo-gambogic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
2-Butenoic acid,4-(3a,4,5,7,10,11-hexahydro-8,9-dihydroxy-3,3,11-trimethyl-13-(3-methyl-2-butenyl)-11-(4-methyl-3-pentenyl)-7,15-dioxo-1,5-methano-1H,3H,9H-furo(3,4-g)pyrano(3,2-b)xanthen-1-yl)-2-methyl
neogambogic acid V1982 (2E)-4-[10,12-Dihydroxy-8,21,21-trimethyl-5-(3-methyl-2-buten-1-yl)-8-(4-methyl-3-penten-1-yl)-14,18-dioxo-3,7,20-trioxahexacyclo[15.4.1.0.0.0.0]docosa-4(13),5,11,15-tetraen-19 
-yl]-2-methyl-2-butenoic acid |
| Description | Neogambogic acid, an active ingredient in garcinia, induces apoptosis and has anticancer effect. Neogambogic acid has significant inhibitory activity toward methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Neogambogic acid inhibits HCT-8, Bel-7402, BGC-823, A549, and A2780 cell proliferation, with an IC50 between 1.75 and 3 μM. Neogambogic acid induces A549 cells apoptosis arrested the cells to G0/G1 phase in vitro[1]. |
| In Vivo | Neogambogic acid arrests A549-induced tumor growth in nude mice[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 810.3±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C38H46O9 |
| Molecular Weight | 646.766 |
| Flash Point | 250.2±27.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 646.314209 |
| PSA | 139.59000 |
| LogP | 8.19 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.627 |