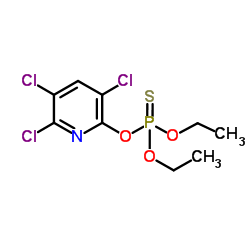
5598-15-2
| Name | Chlorpyrifos-oxon |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Chlorpyrifos Oxon |
| Description | Chlorpyrifos-oxon, an active metabolite of Chlorpyrifos, is a potent phosphorylating agent that potently inhibits AChE. Chlorpyrifos-oxon can induce cross-linking between subunits of tubulin and disrupt microtubule function[1][2][3][4]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Treatment of tubulin with 1.5 mM Chlorpyrifos-oxon (CPO) leads to protein aggregation. However, even at 1.5 μM Chlorpyrifos-oxon cross-linked trimers are apparent. Chlorpyrifos-oxon promotes isopeptide bond cross-linking of tubulin monomers to make multimers[2]. In PC12 cells in culture, 24 hours of exposure to Chlorpyrifos at a concentration 10-fold below the concentration that inhibits AChE activity (3.0 μM) impaired neurite outgrowth while Chlorpyrifos-oxon inhibits neurite outgrowth at 1.0 nM[3]. |
| In Vivo | Chlorpyrifos-oxon (CPO) is rapidly detoxified by human liver microsomes via CYP-dependent deethylation and dearylation, and by glutathione-S-transferase. In addition, reactions with A-esterases such as paraoxonase 1 (PON 1) or B-esterases such as carboxylesterase and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) in the liver may rapidly degrade or scavenge Chlorpyrifos-oxon[1]. Chlorpyrifos-oxon (3 mg/kg, ip; once; wild-type mice) treatment shows the dimensions of microtubules from Chlorpyrifos-oxon-treated mice are about 60% of those from control mice. The microtubules from mice exposed to Chlorpyrifos-oxon have covalently modified amino acids and abnormal structure, suggesting disruption of microtubule function[4]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.461g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 357.8ºC at 760mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C9H11Cl3NO4P |
| Molecular Weight | 334.52100 |
| Flash Point | 170.2ºC |
| Exact Mass | 332.94900 |
| PSA | 67.46000 |
| LogP | 4.60170 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.523 |
| Storage condition | 0-6°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Hazard Codes | T+ |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | UN 2783 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |