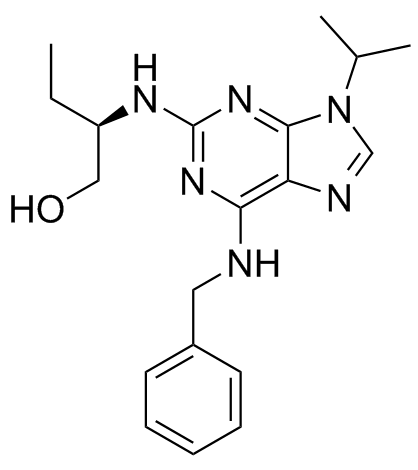
186692-46-6
| Name | seliciclib |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
CYC 202
(2R)-2-{[6-(Benzylamino)-9-isopropyl-9H-purin-2-yl]amino}butan-1-ol P34 CDC2 6-Benzylamino-2[(R)-(1'-ethyl-2'-hydroxyethylamino)]-9-isopropylpurine Roscovitine R-roscovitine (+)-Seliciclib MFCD02266401 (R)-Roscovitine (R)-2-((6-(Benzylamino)-9-isopropyl-9H-purin-2-yl)amino)butan-1-ol (2R)-2-{[6-(benzylamino)-9-(propan-2-yl)-9H-purin-2-yl]amino}butan-1-ol Seliciclib Roscovitine Roscovitin (2R)-2-{[6-(Benzylamino)-9-isopropyl-9H-purin-2-yl]amino}-1-butanol CYC202 CYC202 Cyclacel |
| Description | Roscovitine is a potent and selective CDKs inhibitor with IC50s of 0.2 μM, 0.65 μM, and 0.7 μM for CDK5, Cdc2, and CDK2, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
cdc2/cyclin B:0.65 μM (IC50) cdk2/cyclin A:0.7 μM (IC50) Cdk2/cyclin E2:0.7 μM (IC50) CDK5/p35:0.16 μM (IC50) GST-erk1:30 μM (IC50) erk1:34 μM (IC50) erk2:14 μM (IC50) Insulin-receptor tyrosine kinase:70 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Roscovitine displays high efficiency and high selectivity towards some cyclin-dependent kinases. The kinase specificity of Roscovitine is investigated with 25 highly purified kinases (including protein kinase A, G and C isoforms, myosin light-chain kinase, casein kinase 2, insulin receptor tyrosine kinase, c-src, v-abl). Most kinases are not significantly inhibited by Roscovitine. Cdc2, Cdk2, and Cdk5 only are substantially inhibited (IC50 values of 0.65, 0.7, and 0.2 μM, respectively). Cdk4k and Cdk6 are very poorly inhibited by Roscovitine (IC50>100 μM). Extracellular regulated kinases erk1 and erk2 are inhibited with an IC50 of 34 μM and 14 μM, respectively. Roscovitine inhibits the proliferation of mammalian cell lines with an average IC50 of 16 μM[1]. Roscovitine decreases the level of CDK5 and p35 with upregulation of E-cadherin, but downregulation of Vimentin and Collagen IV. Moreover, Roscovitine inhibits the ability of high glucose cultured NRK52E cells to migrate and invade[2]. |
| In Vivo | Compare with normal controls, Roscovitine downregulates phosphorylated ERK1/2 and PPARγ with concomitant increase in E-cadherin, but decrease in Vimentin and Collagen IV. Correspondingly, Roscovitine decreases renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis of diabetic rats. Roscovitine is effective in decreasing tubulointerstitial fibrosis via the ERK1/2/PPARγ pathway in diabetic rats[2]. Roscovitine (16.5 mg/kg) significantly reduces the rate of tumor growth and increases survival of treated mice. Strikingly, Roscovitine treatment leads to complete tumor disappearance in one mouse (25%); moreover, no tumor regrowth in this mouse is found 5 months after completion of the treatment. Mouse weights do not differ significantly between mice treated with Roscovitine and control mice, and behavioral differences between the two groups are also negligible. These results suggest that Roscovitine can be used effectively as a selective tumor growth inhibitor in HPV+ head and neck cancer[3]. |
| Cell Assay | Rat kidney tubular epithelial cells (NRK52E) are used. CDK5 inhibitor Roscovitine (Ros.; 10 μM) and activator p35 (15 μM), PPARγ agonist Rosiglitazone (Rosi.; 50 nM), and ERK1/2 inhibitor U0126 (50 nM) are used to treat NRK52E cells. Cells in each group are treated for 72 hours and then harvested for further analyses[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats[2] Male Sprague Dawley rats (6-8 weeks of age) are given intraperitoneally a single injection of either Streptozotocin (65 mg/kg) diluted in 0.1 M citrate buffer pH 4.5 (diabetic) or citrate buffer (non-diabetic). Plasma glucose concentrations are determined using the glucose oxidase method on a glucose analyzer three days after the injection. Rats with a glucose level over 16.7 mM are considered diabetic and thus included in the study. Plasma glucose level is measured once every week. To investigate the effect of CDK5 inhibition on renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis, Roscovitine (25 mg/kg) is injected peritoneally to diabetic rats every day till sacrifice. DMSO is included as controls. Mice[3] Exponentially growing UMSCC47 cells are injected subcutaneously into the sacral area of female NUDE mice. Each mouse is inoculated with 2×105 cells in 50% matrigel and 50% PBS at a volume of 100 μL. After tumors reach a measurable size, the mice are given 16.5 mg/kg doses of intraperitoneal Roscovitine or vehicle injections. Body weight, tumor growth, and general behavior are monitored. Tumor volumes are measured every 3 days. Mice are sacrificed when the tumor exceeded a size of 0.5cm3. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 577.5±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C19H26N6O |
| Molecular Weight | 354.449 |
| Flash Point | 303.1±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 354.216797 |
| PSA | 87.89000 |
| LogP | 1.68 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.643 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
| Precursor 6 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |