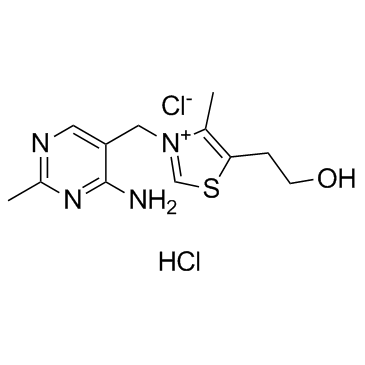
532-43-4
| Name | Thiamine nitrate |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
EINECS 208-537-4
MFCD00036330 Thiamin mononitrate Thiaminenitrate thiamin nitrate Thiamine nitrate,Vitamin B1 nitrate Vitamin B1 Mono thiamine,nitrate Vitamin B1 nitrate Thiamine Nitrate Vitanon Thaimenitrate thiaminium nitrate Thiaminnitrat VitaMin B1 HNO3 mnitrate |
| Description | Thiamine nitrate is an essential vitamin which can enhance normal neuronal actives. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Thiamine levels in the blood of homozygous KO and KI mice fed a conventional diet are decreased to 0.058±0.051 and 0.126±0.092 μM, respectively, at 7 weeks compare to WT mice (0.796±0.259 μM). When WT and homozygous KO and KI mice are fed a Thiamine-restricted diet (Thiamine: 0.60 mg/100 g food), blood Thiamine concentration at 5 and 14 days is markedly decreased to 0.010±0.009 and 0.010±0.006 μM, respectively, compare to WT mice (0.609±0.288 μM). Thiamine concentration in brain homogenate of WT mice fed a conventional diet is 3.81±2.18 nmol/g wet weight, and that of KO and KI is 1.33±0.96 and 2.16±1.55 nmol/g wet weight, respectively. Notably, Thiamine concentration in brain homogenate decreases steadily in KO and KI mice fed a thiamine-restrict diet (Thiamine: 0.60 mg/100 g food) for 5 days (0.95±0.72 nmol/g wet weight) and 14 days (1.11±0.24 nmol/g wet weight), respectively, compare to WT (3.65±1.02 nmol/g wet weight), before the mice presenting an phenotype of disease[2]. |
| In Vivo | WT, homozygous, and heterozygous KO and KI mice fed a conventional diet (thiamine: 1.71 mg/100 g) survive for over 6 months without any phenotype of disease. Homozygous KO and KI mice fed a Thiamine-restricted diet (thiamine: 0.60 mg/100 g food) show paralysis, weight loss, and immobility, and die within 12 and 30 days, respectively. Similarly, homozygous KO and KI mice fed a Thiamine-restricted diet with an even lower percentage of Thiamine (Thiamine: 0.27 mg/100 g food) die within 14 and 18 days, respectively. However, WT and heterozygous KO and KI mice fed a Thiamine-restricted diet (Thiamine: 0.60 mg or 0.27 mg/100g food) survive for over 6 months without any phenotype of disease[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Slc19a3 E314Q KI mice are maintained routinely with conventional diet, which has a Thiamine concentration (thiamine hydrochloride, MW=337.3) of 1.71 mg/100 g food. Two types of Thiamine-restrict food base on “purified diets for laboratory rodents” are prepared, in which Thiamine concentration is 0.60 mg/100 g food (35% Thiamine of conventional food) or 0.27 mg/100 g food (16% Thiamine of conventional food). A high-Thiamine-containing food is also prepared from AIN-93M, in which Thiamine concentration is five times that of CE-2 (thiamine: 8.50 mg/100 g food)[2]. |
| References |
| Melting Point | 196-200°C |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H17N5O4S |
| Molecular Weight | 327.359 |
| Exact Mass | 327.100128 |
| PSA | 173.03000 |
| LogP | 1.47300 |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
|---|---|
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| RTECS | XI7400000 |
| HS Code | 2934100090 |
|
~% 
532-43-4 |
| Literature: Acta Crystallographica, Section C: Crystal Structure Communications, , vol. 50, # 8 p. 1265 - 1267 |
|
~% 
532-43-4 |
| Literature: J. Appl. Chem. USSR (Engl. Transl.), , vol. 34, p. 229 - 232,219 - 221 |
| HS Code | 2934100090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2934100090 other compounds containing an unfused thiazole ring (whether or not hydrogenated) in the structure VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:20.0% |