129580-63-8
| Name | satraplatin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
acetic acid,azane,cyclohexanamine,dichloroplatinum
Platinum(4+) chloride acetate cyclohexanamine ammoniate (1:2:2:1:1) YHI-601 JM-216 Acetic acid, compd. with cyclohexanamine, platinum(4+) salt, hydrochloride, ammoniate (2:1:1:2:1) |
| Description | Satraplatin is an alkylating agent, with potent antitumor effect. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Satraplatin has potent antitumor activity. Satraplatin combined with dichloroacetate (DCA) inhibits UMC-11 cells with an IC50 of 1.36 ± 0.11 μM[1]. Satraplatin also suppresses CDDP-resistant (KB-R) cells (IC50, 7.04 μM), and causes G2/M arrest in KB-R cells[2]. |
| Cell Assay | Cells are harvested, counted and distributed to microtiter plates in 100 μL medium at a density of 1×104 cells/well. Appropriate dilutions of test compounds (Satraplatin, etc.) are added to a total volume of 200 μL/well and plates incubated under tissue culture conditions for four days. Stock solutions of the compounds are prepared in either 70% ethanol or DMSO and diluted more than 100-fold for the assays. Solvent controls are included in all tests. Dose response curves are obtained by assessing cell proliferation at twofold drug dilutions in triplicate and used for calculation of IC50 values. Cell growth is quantified using a modified tetrazolium dye assay (MTT) and by measurement of the reduced formazane dye at 450 nm wavelength (medium control set to 100% proliferation)[1]. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 134.5ºCat 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H22Cl2N2O4Pt |
| Molecular Weight | 500.283 |
| Flash Point | 32.2ºC |
| Exact Mass | 499.060455 |
| PSA | 81.86000 |
| LogP | 3.70610 |
| Vapour Pressure | 8.07mmHg at 25°C |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
|
~70% 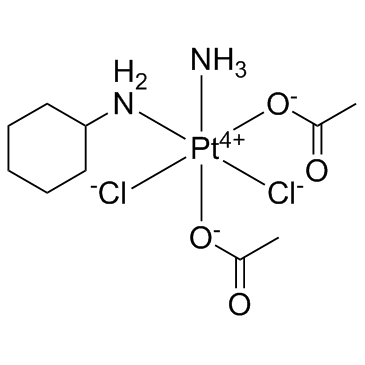
129580-63-8 |
| Literature: Barnard, Christopher F. J.; Vollano, Jean F.; Chaloner, Penny A.; Dewa, Shaliza Z. Inorganic Chemistry, 1996 , vol. 35, # 11 p. 3280 - 3284 |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |