Regorafenib Monohydrate
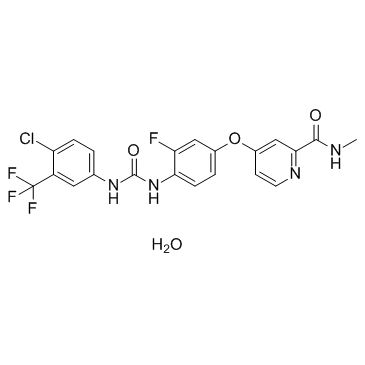
Regorafenib Monohydrate structure
|
Common Name | Regorafenib Monohydrate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1019206-88-2 | Molecular Weight | 500.831 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H17ClF4N4O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Regorafenib MonohydrateRegorafenib monohydrate is a multi-target inhibitor for VEGFR1/2/3, PDGFRβ, Kit, RET and Raf-1 with IC50s of 13/4.2/46, 22, 7, 1.5 and 2.5 nM, respectively. |
| Name | 4-[4-[[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]carbamoylamino]-3-fluorophenoxy]-N-methylpyridine-2-carboxamide,hydrate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Regorafenib monohydrate is a multi-target inhibitor for VEGFR1/2/3, PDGFRβ, Kit, RET and Raf-1 with IC50s of 13/4.2/46, 22, 7, 1.5 and 2.5 nM, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
VEGFR1:13 nM (IC50) VEGFR2:4.2 nM (IC50) VEGFR3:46 nM (IC50) PDGFRβ:22 nM (IC50) Raf-1:2.5 nM (IC50) Braf:28 nM (IC50) BRafV600E:19 nM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Regorafenib potently inhibits VEGFR2 autophosphorylation in NIH-3T3/VEGFR2 cells with an IC50 of 3 nM. In HAoSMCs, regorafenib inhibits PDGFR-β autophosphorylation after stimulation with PDGF-BB, with an IC50 of 90 nM. Regorafenib inhibits the proliferation of VEGF165-stimulated HUVECs, with an IC50 of 3 nM[1]. Regorafenib causes a concentration-dependent decrease in Hep3B cell growth, having an IC50 of 5 μM. Regorafenib subsequently increases the levels of phospho-c-Jun, a JNK target, but not total c-Jun in Hep3B cells[3]. |
| In Vivo | Regorafenib effectively inhibits growth of the Colo-205 xenografts in the dose range of 10-100 mg/kg reaching a TGI of 75% at day 14 at the 10 mg/kg dose. In the MDA-MB-231 model, regorafenib is highly efficacious at a dose as low as 3 mg/kg, resulting in a significant TGI of 81%, which increases to 93% at doses of 10 and 30 mg/kg, where tumor stasis is reached[1]. |
| Kinase Assay | Initial in vitro kinase inhibition profiling is performed at Millipore Corporation at a fixed 1 μM compound concentration under Millipore standard conditions [10 μM adenosine-5′-triphosphate (ATP) concentration]. Inhibitory concentration of 50% (IC50) values are determined from selected responding kinases,e.g., VEGFR1 and RET. TIE2 kinase inhibition is measured with a homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence (HTRF) assay using a recombinant fusion protein of glutathione-S-transferase, the intracellular domain of TIE2 and the peptide biotin-Ahx-EPKDDAYPLYSDFG as substrate[1]. |
| Cell Assay | For proliferation assays, GIST 882 and TT cells are grown in RPMI medium containing L-glutamine, and MDA-MB-231, HepG2 and A375 cells in DMEM always containing 10% hiFBS. Cells are trypsinized, plated at 5×104 cells/well in 96-well plates in complete media containing 10% FBS and grown overnight at 37°C. The next day, vehicle or Regorafenib serially diluted in complete growth media to between 10 μM and 5 nM final concentrations, and 0.2% DMSO, is added and incubation is continued for 96 hr. Cell proliferation is quantified using CellTitre-GloTM[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[1] Female athymic NCr nu/nu mice are subcutaneously inoculated with 5×106 Colo-205 or MDA-MB-231 cells or implanted with 1 mm3 786-O tumor fragments. When tumors reach a volume of 100 mm3, Regorafenib or vehicle control is administered orally qd×21 in the 786-O model, and qd×9 in the Colo-205 and MDA-MB-231 models, respectively, at doses of 100, 30, 10, and 3 mg/kg. Paclitaxel is administered intravenously at 10 mg/kg in ethanol/Cremophor EL®/saline (12.5%/12.5%/75%) every 2 days×5. Tumor size (volume) is estimated twice weekly (l×w2)/2, and the percentage of tumor growth inhibition (TGI) is obtained from terminal tumor weights (1-T/C×100). Mice are weighed every other day starting from the first day of treatment. The general health status of the mice is monitored daily. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C21H17ClF4N4O4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 500.831 |
| Exact Mass | 500.087433 |
| PSA | 105.07000 |
| LogP | 6.10200 |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |
| 2-Pyridinecarboxamide, 4-[4-[[[[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]amino]carbonyl]amino]-3-fluorophenoxy]-N-methyl-, hydrate (1:1) |
| MGN125FS9D |
| regorafenib monohydrate |
| 4-[4-({[4-Chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]carbamoyl}amino)-3-fluorophenoxy]-N-methyl-2-pyridinecarboxamide hydrate (1:1) |
| 4-[4-({[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]carbamoyl}amino)-3-fluorophenoxy]-N-methylpyridine-2-carboxamide monohydrate |
| Regorafenib (monohydrate) |
| Regorafenib hydrate [JAN] |
| bay 73-4506 monohydrate |
| UNII-MGN125FS9D |
| 4-[4-({[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl) phenyl] carbamoyl} amino)-3-fluorophenoxy]-N-methylpyridine-2-carboxamide monohydrate |
| Stivarga |
| regorafenib hydrate |
| 4-[4-({[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]carbamoyl}amino)-3-fluorophenoxy]-pyridine-2-carboxylic acid methylamide monohydrate |
| Stivarga (TN) |

