chloranilic acid barium salt trihydrate
Modify Date: 2025-08-24 12:24:18
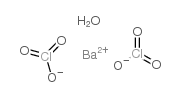
chloranilic acid barium salt trihydrate structure
|
Common Name | chloranilic acid barium salt trihydrate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 10294-38-9 | Molecular Weight | 322.24500 | |
| Density | 3.18 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | BaCl2H2O7 | Melting Point | 414 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |



GHS03, GHS07, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | chloranilic acid barium salt trihydrate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 3.18 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 414 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | BaCl2H2O7 |
| Molecular Weight | 322.24500 |
| Exact Mass | 321.82300 |
| PSA | 123.63000 |
| LogP | 0.60190 |
| Appearance of Characters | white monoclinic crystals |
|
Section 1. Chemical Product and Company Identification Barium Chlorate, Monohydrate Common Name/ Trade Name Barium Chlorate, Monohydrate Potential Chronic HealthCARCINOGENIC EFFECTS: Not available. MUTAGENIC EFFECTS: Not available.
Effects TERATOGENIC EFFECTS: Not available. DEVELOPMENTAL TOXICITY: Not available. The substance may be toxic to blood, kidneys, lungs. Repeated or prolonged exposure to the substance can produce target organs damage. Section 4. First Aid Measures Eye ContactCheck for and remove any contact lenses. In case of contact, immediately flush eyes with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes. Cold water may be used. Get medical attention. Skin ContactIn case of contact, immediately flush skin with plenty of water. Cover the irritated skin with an emollient. Remove contaminated clothing and shoes. Cold water may be used.Wash clothing before reuse. Thoroughly clean shoes before reuse. Get medical attention. Serious Skin ContactWash with a disinfectant soap and cover the contaminated skin with an anti-bacterial cream. Seek immediate medical attention. InhalationIf inhaled, remove to fresh air. If not breathing, give artificial respiration. If breathing is difficult, give oxygen. Get medical attention. Serious InhalationEvacuate the victim to a safe area as soon as possible. Loosen tight clothing such as a collar, tie, belt or waistband. If breathing is difficult, administer oxygen. If the victim is not breathing, perform mouth-to-mouth resuscitation. WARNING: It may be hazardous to the person providing aid to give mouth-to-mouth resuscitation when the inhaled material is toxic, infectious or corrosive. Seek medical attention. IngestionDo NOT induce vomiting unless directed to do so by medical personnel. Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. If large quantities of this material are swallowed, call a physician immediately. Loosen tight clothing such as a collar, tie, belt or waistband. Serious IngestionNot available. Section 5. Fire and Explosion Data Flammability of the Product Non-flammable. Auto-Ignition Temperature Not applicable. Flash PointsNot applicable. Flammable LimitsNot applicable. Products of CombustionNot available. Fire Hazards in Presence of of organic materials of combustible materials Various Substances Explosion Hazards in Presence Risks of explosion of the product in presence of static discharge: Not available. of Various SubstancesSlightly explosive in presence of shocks, of heat, of combustible materials, of organic materials. Fire Fighting MediaNot applicable. and Instructions Special Remarks onPowerful oxidizing agent; may ignite oxidizable materials. Contact with combustible or organic materials may Fire Hazardscause fire. A mixture of sulfur and barium chlorate ignites at about 108-111 C. Contact with strong sulfuric acid can cause fires or explosions. When mixed with ammonium salts, spontaneous decomposition and ignition may result. Special Remarks on Explosion A combination of finely divided aluminum, arsenic, carbon, copper, metal sulfides, organic matter, Hazardsphosphorus, or sulfur with finely divided chlorates of barium can be exploded by heat, percussion, and sometimes light friction. Contact with strong sulfuric acid can cause fires or explosions. Mixtures of finely divided combustible materials (such as certain dusty forms of floor sweepings/saw dust), charcoal with chlorates can explode virtually spontaneously. Chlorates can also present a dangerous explosion hazard when shocked, exposed to heat, or rubbed, particularly when contaminated with As2S3, CaH2, Hg3P4, Manganese dioxide, NaH2PO2, PHI4, SCN, ammonium compounds, cyanides, metals + acids, organic acids, phosphorus or antimony sulfide, selenium, shellac, starch, sugar. Barium Chlorate, Monohydrate Section 6. Accidental Release Measures Small SpillUse appropriate tools to put the spilled solid in a convenient waste disposal container. Large SpillOxidizing material. Organic peroxide. Stop leak if without risk. Avoid contact with a combustible material (wood, paper, oil, clothing...). Keep substance damp using water spray. Do not use metal tools or equipment. Do not touch spilled material. Use for assistance on disposal. Be careful that the product is not present at a concentration level above TLV. Check TLV on the MSDS and with local authorities. Section 7. Handling and Storage PrecautionsKeep away from heat. Keep away from sources of ignition. Keep away from combustible material.. Do not ingest. Do not breathe dust. Wear suitable protective clothing. If ingested, seek medical advice immediately and show the container or the label. Avoid contact with skin and eyes. Keep away from incompatibles such as reducing agents, combustible materials, organic materials, metals, acids. StorageKeep container tightly closed. Keep container in a cool, well-ventilated area. Separate from acids, alkalies, reducing agents and combustibles. See NFPA 43A, Code for the Storage of Liquid and Solid Oxidizers. Section 8. Exposure Controls/Personal Protection Engineering ControlsUse process enclosures, local exhaust ventilation, or other engineering controls to keep airborne levels below recommended exposure limits. If user operations generate dust, fume or mist, use ventilation to keep exposure to airborne contaminants below the exposure limit. Personal ProtectionSplash goggles. Lab coat. Dust respirator. Be sure to use an approved/certified respirator or equivalent. Gloves. Personal Protection in Case of Splash goggles. Full suit. Dust respirator. Boots. Gloves. A self contained breathing apparatus should be a Large Spillused to avoid inhalation of the product. Suggested protective clothing might not be sufficient; consult a specialist BEFORE handling this product. TWA: 0.5 (mg(Ba)/m3) from OSHA (PEL) [United States] Exposure Limits Consult local authorities for acceptable exposure limits. Section 9. Physical and Chemical Properties Physical state and appearance Solid. (Crystals solid. Powdered solid.)Odorless. Odor TasteNot available. Molecular Weight322.26 g/mole ColorWhite. pH (1% soln/water)Not available. Boiling PointNot available. 250°C (482°F) Melting Point Critical TemperatureNot available. Density: 3.179 (Water = 1) Specific Gravity Not applicable. Vapor Pressure Vapor DensityNot available. VolatilityNot available. Odor ThresholdNot available. Water/Oil Dist. Coeff.Not available. Not available. Ionicity (in Water) Dispersion PropertiesSee solubility in water. SolubilitySoluble in cold water. Very slightly soluble in acetone. Solubility in Water: 27.4 g/100 ml water at 15 deg. C.; 111.2 g/100 ml water at 100 deg. C. Slightly soluble in alcohol, Hydrochloric acid. Moderately soluble in Ethylamine. Practically insoluble in Ethyl acetate, Pyridine. Barium Chlorate, Monohydrate Section 10. Stability and Reactivity Data The product is stable. Stability Instability TemperatureNot available. Conditions of InstabilityIncompatible materials Incompatibility with variousHighly reactive with reducing agents, combustible materials, organic materials, metals, acids. substances Not available. Corrosivity Special Remarks onLoses its water of hydration at 120 C. Gives off oxygen at 250 C. ReactivityIncompatible with combustible materials (oil, wood, paper, leather, chlothing), finely powedered metals, aluminum Not available. Special Remarks on Corrosivity PolymerizationWill not occur. Section 11. Toxicological Information Routes of EntryInhalation. Ingestion. Toxicity to AnimalsLD50: Not available. LC50: Not available. Chronic Effects on Humans May cause damage to the following organs: blood, kidneys, lungs. Other Toxic Effects onHazardous in case of skin contact (irritant), of ingestion. HumansSlightly hazardous in case of inhalation. Special Remarks onNot available. Toxicity to Animals Special Remarks onNot available. Chronic Effects on Humans Special Remarks on otherAcute Potential Health Effects: Toxic Effects on HumansSkin: Causes skin irritation. Eyes: Causes eye irritation. Inhalation: May cause respiratory tract irritation. Ingestion: Harmful if swallowed. Causes abdominal cramping, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea or colic. In very acute or fatal cases the following may occur: pale complexion (pallor), hypotension (low blood pressure), irregular heartbeat, hemolysis with methemoglobin formation which reduces the oxygen carrying capacity of the blood resulting in cyanosis(a bluish discoloration of the skin, and lips), seizures, tremors, muscle twitching, headache, fatigue, dizziness, trouble breathing, leukocytosis, thrombocytopenic disorder. In chlorate poisoning, early death is usually due to anoxia. Renal failure and hyperkalemia may also occur. Later death is generally due to renal failure. Section 12. Ecological Information EcotoxicityNot available. BOD5 and CODNot available. Possibly hazardous short term degradation products are not likely. However, long term degradation products Products of Biodegradation may arise. The products of degradation are less toxic than the product itself. Toxicity of the Products of Biodegradation Special Remarks on theNot available. Products of Biodegradation Barium Chlorate, Monohydrate Section 13. Disposal Considerations Waste DisposalWaste must be disposed of in accordance with federal, state and local environmental control regulations. Section 14. Transport Information DOT Classification CLASS 5.1: Oxidizing material. CLASS 6.1: Poisonous material. : Barium Chlorate, solid UNNA: 1445 PG: II Identification Special Provisions forNot available. Transport DOT (Pictograms) OXIDIZER 5.1 Section 15. Other Regulatory Information and Pictograms Pennsylvania RTK: Barium Chlorate, Monohydrate Federal and State Minnesota: Barium Chlorate, Monohydrate Regulations New Jersey: Barium Chlorate, Monohydrate New Jersey spill list: Barium Chlorate, Monohydrate Louisiana spill reporting: Barium Chlorate, Monohydrate California Director's List of Hazardous Substances: Barium Chlorate, Monohydrate SARA 313 toxic chemical notification and release reporting: Barium Chlorate, Monohydrate CaliforniaCalifornia prop. 65: This product contains the following ingredients for which the State of California has Proposition 65found to cause cancer which would require a warning under the statute: No products were found. Warnings California prop. 65: This product contains the following ingredients for which the State of California has found to cause birth defects which would require a warning under the statute: No products were found. Other RegulationsOSHA: Hazardous by definition of Hazard Communication Standard (29 CFR 1910.1200). For CAS number 13477-00-4 (anhydrous form): EINECS: This product is on the European Inventory of Existing Commercial Chemical Substances. (EINECS No. 236-760-7) Canada: Listed on Canadian Non-Domestic Substance List (NDSL). China: Listed on National Inventory. Japan: Listed on National Inventory (ENCS). Korea: Listed on National Inventory (KECI). Philippines: Not listed on National Inventory (PICCS). Australia: Listed on AICS. CAS number 10294-38-9(monohydrate form) is not on the following inventories: European (EINECS), Canadian NDSL/DSL, China, Japan (ENCS), or Australia (AICS). CAS number 10294-38-9(monohydrate form) is on the following inventories: Korea (KECI), Philippines (PICCS) CLASS C: Oxidizing material. Other ClassificationsWHMIS (Canada) CLASS D-1A: Material causing immediate and serious toxic effects (VERY TOXIC). DSCL (EEC)R9- Explosive when mixed withS13- Keep away from food, drink and animal combustible material.feedingstuffs. R20/22- Harmful by inhalation and ifS27- Take off immediately all contaminated swallowed.clothing. R51/53- Toxic to aquatic organisms,S61- Avoid release to the environment. Refer may cause long-term adverse effectsto special instructions/Safety data sheets. in the aquatic environment. Health Hazard HMIS (U.S.A.)2 National Fire Protection 0 Flammability 0 Association (U.S.A.) Fire Hazard 2 0 Reactivity Health Reactivity 1 Specific hazard Personal Protection E Barium Chlorate, Monohydrate WHMIS (Canada) (Pictograms) DSCL (Europe) (Pictograms) TDG (Canada) (Pictograms) 5.1 ADR (Europe) (Pictograms) Protective Equipment Gloves. Lab coat. Dust respirator. Be sure to use an approved/certified respirator or equivalent. Wear appropriate respirator when ventilation is inadequate. SECTION 16 - ADDITIONAL INFORMATION N/A |
| Symbol |



GHS03, GHS07, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H271-H302 + H332-H411 |
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P220-P221-P261-P370 + P378-P371 + P380 + P375 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | Xn,N,O |
| Risk Phrases | R20/22 |
| Safety Phrases | S28-S61-S27-S13 |
| RIDADR | UN 1564 6.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| Hazard Class | 5.1 |
| HS Code | 2829199000 |
| HS Code | 2829199000 |
|---|
| BariuM chlorate Monohydrate |
| Chloranilic acid barium salt monohydrate |
| CHLORANILIC ACID,BARIUM SALT |
| EINECS 236-760-7 |
| BariumchlorateH2O |
| BARIUMCHLORATEMONOHYDRATE,CRYSTAL,REAGENT |
| BARIUM CHLOROANILATE TRIHYDRATE |
| BARIUM CHLORATE 1-HYDRATE |
| Chloric acid,barium salt,monohydrate |
| BARIUM CHLORANILATE TRIHYDRATE |
| MFCD00150175 |