Colestyramine
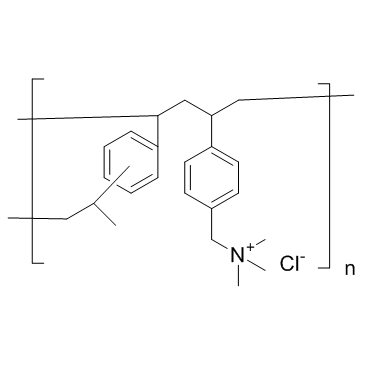
Colestyramine structure
|
Common Name | Colestyramine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 11041-12-6 | Molecular Weight | 331.923 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H30ClN | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of ColestyramineColestyramine (Cholestyramine) is a bile acid binding resin and can inhibit intestinal bile acid absorption which results in the increasing bile acid synthesis from cholesterol. |
| Name | cholestyramine resin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Colestyramine (Cholestyramine) is a bile acid binding resin and can inhibit intestinal bile acid absorption which results in the increasing bile acid synthesis from cholesterol. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vivo | Colestyramine (Cholestyramine) is a bile acid binding resin and can inhibit intestinal bile acid absorption which results in the increasing bile acid synthesis from cholesterol[1]. Results reveal that GSPE treatment alone, and co-administration with Colestyramine (CHY), regulate BA, cholesterol and TG metabolism differently compare to Colestyramine (CHY) administration alone. Notably, GSPE decreases intestinal apical sodium-dependent bile acid transporter (Asbt) gene expression, while Colestyramine (CHY) significantly induces expression. Administration with GSPE or Colestyramine (CHY) robustly induces hepatic BA biosynthetic gene expression, especially cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase (Cyp7a1), compare to control, while co-administration further enhances expression. Treatment with Colestyramine (CHY) induces both intestinal and hepatic cholesterologenic gene expression, while co-administration with GSPE attenuates the Colestyramine (CHY)-inducing increase in the liver but not in the intestine. Colestyramine (CHY) also induces hepatic lipogenic gene expression, which is attenuated by co-administration with GSPE[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice are purchased at 7 weeks of age and allowed to acclimate for one week. At 8-weeks of age the mice are given either a control or a 2% Colestyramine (cholestyramine)-supplementing diet for 4 weeks (n=18 per group). Body weight for each mouse is recorded weekly. After 4 weeks, the mice in each group are randomly assigned to one of two treatment groups and orally gavaged with either vehicle (water) or GSPE (250 mg/kg) and terminated 14 hours later (n=9 per experimental group). The four treatment groups are as follows: 1. CON: Control diet for 4 weeks following by oral gavage with vehicle (water) for 14 hrs; 2. GSPE: Control diet for 4 weeks following by oral gavage with 250 mg/kg GSPE for 14 hrs; 3.CHY Colestyramine (cholestyramine): 2% Colestyramine (cholestyramine)-supplementing diet for 4 weeks following by oral gavage with vehicle for 14 hrs; and 4. CHY Colestyramine (cholestyramine)+GSPE: 2% cholestyramine-supplementing diet for 4 weeks following by oral gavage with 250 mg/kg GSPE for 14 hrs. Blood is collected from the orbital plexus under isoflurane anesthesia, and intestines and livers are snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at -80°C until use. At the start of the 14 hr experiment mice are placed into clean cages, and feces are manually collected at the end of the study[2]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C21H30ClN |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 331.923 |
| Exact Mass | 331.206665 |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble in water, in methylene chloride and in ethanol (96 per cent). |
|
A review of the diagnosis and treatment of Ochratoxin A inhalational exposure associated with human illness and kidney disease including focal segmental glomerulosclerosis.
J. Environ. Public Health 2012 , 835059, (2012) Ochratoxin A (OTA) exposure via ingestion and inhalation has been described in the literature to cause kidney disease in both animals and humans. This paper reviews Ochratoxin A and its relationship t... |
|
|
Using resin to generate a non-invasive intestinal bile-depleted rat model was unsuccessful.
Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 47(2) , 347-51, (2012) The purpose of this study was to evaluate if a rat model, based upon co-administration of the anion-exchanging resin, cholestyramine, could replace surgery when evaluating the importance of bile on dr... |
|
|
[Antidiarrheal drugs for chronic diarrhea].
Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 138(45) , 2309-12, (2013) Chronic diarrhea can be caused by multiple disease entities. Basic diagnostic tests are required in order to administer specific therapies whenever possible. If no specific treatment can be used, a sy... |
| colestyramin |
| CHOLESTYRAMINE RESIN |
| 4-[3-(4-Ethylphenyl)butyl]-N,N,N-trimethylanilinium chloride |
| Benzenaminium, 4-[3-(4-ethylphenyl)butyl]-N,N,N-trimethyl-, chloride (1:1) |
| cholestyraminechloride |
| cuemid |
| polystyrenebenzyltrimethylaminoniumchloride |
| quantalan |
| MFCD00130784 |
| CHOLESTYRAMINE |
| EINECS 234-270-8 |
| DOWEX 1 X 2 CL-FORM |
| Colestyramine |