Methyl stearate
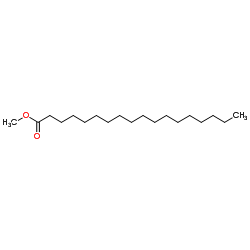
Methyl stearate structure
|
Common Name | Methyl stearate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 112-61-8 | Molecular Weight | 298.504 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 181-182 ºC (4 mmHg) | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H38O2 | Melting Point | 37-41 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 110 ºC | |
Use of Methyl stearateMethyl stearate, isolated from Rheum palmatum L. is a compopent of of soybean and rapeseed biodiesels[1]. |
| Name | methyl stearate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Methyl stearate, isolated from Rheum palmatum L. is a compopent of of soybean and rapeseed biodiesels[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 181-182 ºC (4 mmHg) |
| Melting Point | 37-41 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C19H38O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 298.504 |
| Flash Point | 110 ºC |
| Exact Mass | 298.287170 |
| PSA | 26.30000 |
| LogP | 8.68 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.444 |
| InChIKey | HPEUJPJOZXNMSJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OC |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
|---|---|
| Risk Phrases | R40 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | WI4460000 |
| HS Code | 2915709000 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2915709000 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2915709000. palmitic acid and its salts and esters. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:5.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Gas chromatography with parallel hard and soft ionization mass spectrometry.
Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 29(1) , 91-9, (2014) Mass spectrometric identification of compounds in chromatography can be obtained from molecular masses from soft ionization mass spectrometry techniques such as field ionization (FI) and fragmentation... |
|
|
Optimization of supercritical fluid consecutive extractions of fatty acids and polyphenols from Vitis vinifera grape wastes.
J. Food Sci. 80(1) , E101-7, (2015) In this study, supercritical fluid extraction has been successfully applied to a sequential fractionation of fatty acids and polyphenols from wine wastes (2 different vitis vinifera grapes). To this a... |
|
|
Capillary atmospheric pressure chemical ionization using liquid point electrodes.
Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 28(14) , 1591-600, (2014) Atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) sources operated with point to plane DC discharges ('Coronas') frequently suffer from point electrode degradation and potentially lead to oxidation and/... |
| 3-Aminobenzoic acid |
| METHYLSTEARAT |
| N-OCTADECANOIC ACID METHYL ESTER |
| n-Octadecanoic acid, methyl ester |
| methyl octadecanoate |
| Methyl n-octadecanoate |
| stearic acid methyl ester |
| Methyl ester of octadecanoic acid |
| Mehtyl Stearate |
| Octadecanoic acid, methyl ester |
| Methyl octadecanoate,Stearic acid methyl ester |
| Octadecanoic acid methyl ester |
| UNII-8D4NXF3ZH7 |
| Stearic acid, methyl ester |
| Methyl Stearate |
| Methyloctadecanoate |
| Methyl octadec |
| MFCD00009005 |
| EINECS 203-990-4 |
 CAS#:112-62-9
CAS#:112-62-9 CAS#:67-56-1
CAS#:67-56-1 CAS#:57-11-4
CAS#:57-11-4 CAS#:822-16-2
CAS#:822-16-2 CAS#:638-08-4
CAS#:638-08-4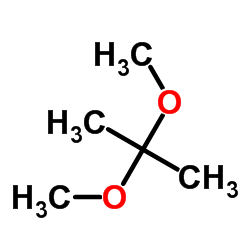 CAS#:77-76-9
CAS#:77-76-9 CAS#:301-00-8
CAS#:301-00-8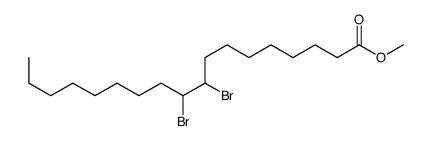 CAS#:25456-04-6
CAS#:25456-04-6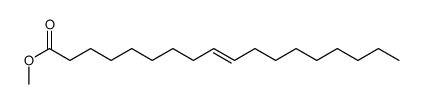 CAS#:2462-84-2
CAS#:2462-84-2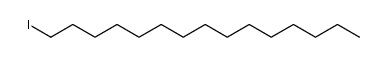 CAS#:35599-78-1
CAS#:35599-78-1 CAS#:109-36-4
CAS#:109-36-4 CAS#:4130-54-5
CAS#:4130-54-5 CAS#:35602-69-8
CAS#:35602-69-8 CAS#:593-45-3
CAS#:593-45-3 CAS#:34557-54-5
CAS#:34557-54-5 CAS#:629-78-7
CAS#:629-78-7 CAS#:201230-82-2
CAS#:201230-82-2 CAS#:1560-92-5
CAS#:1560-92-5 CAS#:1560-89-0
CAS#:1560-89-0
