Ramatroban
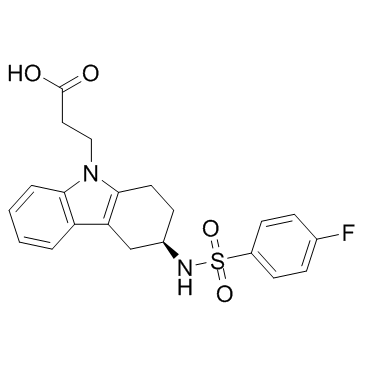
Ramatroban structure
|
Common Name | Ramatroban | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 116649-85-5 | Molecular Weight | 416.466 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 654.7±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H21FN2O4S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 349.7±34.3 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of RamatrobanRamatroban is a selective thromboxane A2 (TxA2, IC50=14 nM) antagonist, which also antagonizes CRTH2 (IC50=113 nM) by inhibiting PGD2 binding. |
| Name | Ramatroban |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Ramatroban is a selective thromboxane A2 (TxA2, IC50=14 nM) antagonist, which also antagonizes CRTH2 (IC50=113 nM) by inhibiting PGD2 binding. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
hTP:14 nM (IC50) hDP2:311 nM (IC50) CYP 2C9:15 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Ramatroban is a potent human thromboxane receptor (hTP) antagonist with an IC50 of 18 nM in a human TP binding assay. Ramatroban inhibits prostaglandin D2 receptor DP2 (CRTH2) with an IC50 of 113 nM in a human DP2 binding assay. Ramatroban also inhibits human CYP isoform CYP2C9 with an IC50 of 15 μM[1]. Ramatroban is a selective thromboxane-type prostanoid (TP) receptor antagonist. PGD2-stimulated human eosinophil migration is shown to be mediated exclusively through activation of CRTH2, and surprisingly, these effects are completely inhibited by Ramatroban. Ramatroban is an antagonist for CRTH2, and inhibits PGD2-induced migration of eosinophils via CRTH2 blockade. 3H-labeled PGD2 binds to a single site on CRTH2 transfectants with high affinity (KD=6.3 nM, Bmax=450 pM). Nonlabeled PGD2 inhibits the binding of 3H-labeled PGD2 to CRTH2 transfectants in a concentration-dependent manner with an EC50 value of 2.7 nM. Ramatroban shows significant inhibitory effects on the binding of 3H-labeled PGD2 to CRTH2, albeit with much lower potency (IC50=100 nM). Ramatroban also inhibits PGD2-induced Ca2+ mobilization in CRTH2 transfectants to almost the same extent with an IC50 value of 30 nM. Ramatroban completely inhibits the PGD2-induced migration of eosinophils in a concentration-dependent manner with an IC50 value of 170 nM[2]. |
| In Vivo | Ramatroban is an orally bioavailable small molecule antagonist of CRTH2. Systemic administration of Ramatroban (30 mg/kg) in CRTH2+/+ mice produces the same effects as seen in CRTH2 deficiency. Ramatroban completely blocks LPS-induced decreases in social and object exploratory behavior (p<0.01). In addition, tumor-impaired social interaction and object exploratory behavior in CRTH2+/+ mice are completely reversed by a single injection of Ramatroban, even when the tumor is enlarged[3]. |
| Kinase Assay | CRTH2 transfectants are resuspended in binding buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, 40 mM MgCl2, 0.1% BSA, 0.1% NaN3). Cell suspension (2×105 cells), 3H-labeled PGD2, and various concentrations of Ramatroban (0.1 nM, 1 nM, 10 nM, 100 nM, 1 μM and 10 μM) are then mixed in a 96-well U-bottomed polypropylene plate and incubated in a final volume of 100 μL for 60 min at room temperature. After incubation, the cell suspension is transferred to a filtration plate and washed three times with binding buffer. Scintillant is added to the filtration plate, and radioactivity remaining on the filter is measured by a scintillation counter. Nonspecific binding is determined by incubating the cell suspension and 3H-labeled PGD2 in the presence of 1 μM unlabeled PGD2[2]. |
| Cell Assay | Human eosinophils are purified and resuspended in migration buffer (20 mM HEPES, pH 7.6, 0.1% BSA, Hanks' solution) at a density of 6 ×106 cells/mL. Fifty microliters of the cell suspension (3×105 cells/well) is then dispensed into the upper chamber of a 96-well type chemotaxis chamber (pore diameter=5 μm), and 30 μL of ligand solution is added to the lower chamber. Cells are preincubated with various concentrations of Ramatroban (0.1 nM, 1 nM, 10 nM, 100 nM, 1 μM and 10 μM) or BWA868C at 37°C for 10 min. The migration assays are performed in a humidified incubator at 37°C, 5% CO2 for 2 h. The number of cells migrating into the lower chamber is counted[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[3] Five micrograms of LPS (closed columns) or saline (open columns) are intraperitoneally injected into CRTH2+/+ mice. CRTH2+/+ mice are pretreated intraperitoneally for 1 h with 30 mg/kg Ramatroban. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 654.7±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C21H21FN2O4S |
| Molecular Weight | 416.466 |
| Flash Point | 349.7±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 416.120605 |
| PSA | 96.78000 |
| LogP | 4.09 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.664 |
| Storage condition | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Phrases | 36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-36/37/39-45 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
|
Interactive effect of histamine and prostaglandin D2 on nasal allergic symptoms in rats.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 554(2-3) , 229-34, (2007) This study was undertaken to investigate the interactive effect of histamine and prostaglandin D(2) in nasal allergic symptoms in rats. The intranasal application of histamine at doses lower than 10 m... |
|
|
IL-16 variability and modulation by antiallergic drugs in a murine experimental allergic rhinitis model.
Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 149(4) , 315-22, (2009) Interleukin-16 (IL-16) is a cytokine that induces selective migration of CD4+ cells and participates in inflammatory diseases including allergic rhinitis. Histamine and prostaglandin D(2) are importan... |
|
|
Successful treatment of eosinophilic otitis media using ramatroban: report of two cases.
Auris. Nasus. Larynx. 33(4) , 455-60, (2006) The pathogenesis of eosinophilic otitis media is not yet fully understood. The purpose of this paper is to describe the clinical course of our two patients with eosinophilic otitis media and to discus... |
| MFCD00887606 |
| 9H-Carbazole-9-propanoic acid, 3-[[(4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl]amino]-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-, (3R)- |
| 3-[(3R)-3-{[(4-Fluorophenyl)sulfonyl]amino}-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-9H-carbazol-9-yl]propanoic acid |
| BAY u 3405 |
| (+)-(3R)-3-(p-Fluorobenzenesulfonamido)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrocarbazole-9-propionic acid |
| Baynas |
| 3-((3R)-3-(((4-Fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)amino)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-9H-carbazol-9-yl)propanoic Acid |
| BAY u-3405 |
| Ramatroban |
| 3-[(3R)-3-[(4-fluorophenyl)sulfonylamino]-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrocarbazol-9-yl]propanoic acid |
![(R)-N-[9-(2-cyanoethyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazol-3-yl]-4-fluorobenzenesulfonamide Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/347/118699-38-0.png) CAS#:118699-38-0
CAS#:118699-38-0 CAS#:51145-61-0
CAS#:51145-61-0![1,4-Dioxaspiro[4.5]decan-8-one Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/201/4746-97-8.png) CAS#:4746-97-8
CAS#:4746-97-8 CAS#:128432-38-2
CAS#:128432-38-2 CAS#:100-63-0
CAS#:100-63-0 CAS#:54621-12-4
CAS#:54621-12-4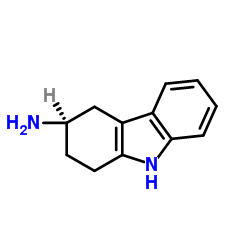 CAS#:116650-33-0
CAS#:116650-33-0 CAS#:1374648-14-2
CAS#:1374648-14-2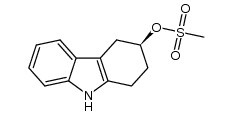 CAS#:1374648-17-5
CAS#:1374648-17-5
