Ferric ammonium citrate
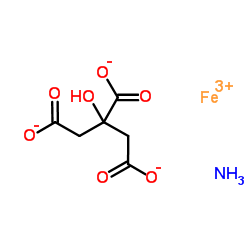
Ferric ammonium citrate structure
|
Common Name | Ferric ammonium citrate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1185-57-5 | Molecular Weight | 261.975 | |
| Density | 1.8 g/cm3 (20ºC) | Boiling Point | 197ºC | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H8FeNO7 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Ferric ammonium citrateAmmonium iron(III) citrate (Ammonium ferric citrate), a physiological form of nonetransferrin-bound iron, induces intracellular iron overload to cause ferroptosis[1]. Ammonium iron(III) citrate can enhance protein production[2]. |
| Name | Ammonium ferric citrate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Ammonium iron(III) citrate (Ammonium ferric citrate), a physiological form of nonetransferrin-bound iron, induces intracellular iron overload to cause ferroptosis[1]. Ammonium iron(III) citrate can enhance protein production[2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Ammonium iron(III) citrate (Ammonium ferric citrate; 1, 5, 10, 15 mM; 24 hours) with 5 mM induces cell death in HT1080 cells. AML12 cells were highly resistant to Ammonium iron(III) citrate, as they maintained cell viability about 80%. Ammonium iron(III) citrate can be actively transported into cells by specific transporter[1]. Ammonium iron(III) citrate (6, 12, 18 mg/L) has a higher biomas for Chlorella vulgaris FSP-E (CV) in BG-11 medium with 12 mg/L and 18 mg/L[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.8 g/cm3 (20ºC) |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 197ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C6H8FeNO7 |
| Molecular Weight | 261.975 |
| Exact Mass | 261.965027 |
| PSA | 102.37000 |
| InChIKey | AUALKMYBYGCYNY-UHFFFAOYSA-E |
| SMILES | O=C([O-])CC(O)(CC(=O)[O-])C(=O)[O-].O=C([O-])CC(O)(CC(=O)[O-])C(=O)[O-].O=C([O-])CC(O)(CC(=O)[O-])C(=O)[O-].O=C([O-])CC(O)(CC(=O)[O-])C(=O)[O-].[Fe+3].[Fe+3].[Fe+3].[NH4+].[NH4+].[NH4+] |
| Water Solubility | 1200 g/L (20 ºC) |
Synonym:Ferric Ammonium Citrate, Citric Acid Ammonium Iron (3+) Salt Section 2 - COMPOSITION, INFORMATION ON INGREDIENTS
Risk Phrases: None Listed. Section 3 - HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION EMERGENCY OVERVIEW
Not available. Potential Health Effects Eye: May cause irritation, pain, blurred vision, and possible burns. Skin: May cause skin irritation. Ingestion: May cause irritation of the digestive tract. Inorganic iron compounds may cause gastrointestinal irritation and damage, vomiting, pulmonary edema, convulsions, rapid heart beat and low blood pressure. Ingestion of iron compounds may cause hemorrhage and necrosis of the stomach with shock, severe diarrhea, and possible coma. Inhalation: May cause respiratory tract irritation. Chronic: No information found. Section 4 - FIRST AID MEASURES Eyes: Immediately flush eyes with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes, occasionally lifting the upper and lower eyelids. Get medical aid immediately. Skin: Get medical aid. Flush skin with plenty of soap and water for at least 15 minutes while removing contaminated clothing and shoes. Wash clothing before reuse. Ingestion: If victim is conscious and alert, give 2-4 cupfuls of milk or water. Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Get medical aid immediately. Inhalation: Get medical aid immediately. Remove from exposure to fresh air immediately. If not breathing, give artificial respiration. If breathing is difficult, give oxygen. Notes to Physician: Antidote: The use of Deferoxamine as a chelating agent should be determined only by qualified medical personnel. Section 5 - FIRE FIGHTING MEASURES General Information: As in any fire, wear a self-contained breathing apparatus in pressure-demand, MSHA/NIOSH (approved or equivalent), and full protective gear. During a fire, irritating and highly toxic gases may be generated by thermal decomposition or combustion. Extinguishing Media: Use water spray, dry chemical, carbon dioxide, or appropriate foam. Section 6 - ACCIDENTAL RELEASE MEASURES General Information: Use proper personal protective equipment as indicated in Section 8. Spills/Leaks: Clean up spills immediately, observing precautions in the Protective Equipment section. Sweep up, then place into a suitable container for disposal. Avoid generating dusty conditions. Provide ventilation. Section 7 - HANDLING and STORAGE Handling: Wash thoroughly after handling. Remove contaminated clothing and wash before reuse. Use with adequate ventilation. Minimize dust generation and accumulation. Avoid contact with skin and eyes. Avoid ingestion and inhalation. Storage: Store in a cool, dry place. Do not store in direct sunlight. Keep containers tightly closed. Section 8 - EXPOSURE CONTROLS, PERSONAL PROTECTION Engineering Controls: Use adequate ventilation to keep airborne concentrations low. Personal Protective Equipment Eyes: Wear appropriate protective eyeglasses or chemical safety goggles as described by OSHA's eye and face protection regulations in 29 CFR 1910.133 or European Standard EN166. Skin: Wear appropriate protective gloves to prevent skin exposure. Clothing: Wear appropriate protective clothing to prevent skin exposure. Respirators: Follow the OSHA respirator regulations found in 29CFR 1910.134 or European Standard EN 149. Always use a NIOSH or European Standard EN 149 approved respirator when necessary. Section 9 - PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES Physical State: Solid Appearance: yellow to green Odor: None reported pH: Not available. Vapor Pressure: Not available. Viscosity: Not available. Boiling Point: Decomposes. Freezing/Melting Point: Decomposes. Autoignition Temperature: Not applicable. Flash Point: Not applicable. Explosion Limits, lower: Not available. Explosion Limits, upper: Not available. Decomposition Temperature: Not available. Solubility in water: Soluble. Specific Gravity/Density: 1.8 @ 20C Molecular Formula: Mixture Molecular Weight: 0 Section 10 - STABILITY AND REACTIVITY Chemical Stability: Stable under normal temperatures and pressures. Conditions to Avoid: Incompatible materials, light, excess heat. Incompatibilities with Other Materials: Strong oxidizing agents - light. Hazardous Decomposition Products: Ammonia. Hazardous Polymerization: Has not been reported. Section 11 - TOXICOLOGICAL INFORMATION RTECS#: CAS# 1185-57-5: GE7540000 LD50/LC50: Not available. Carcinogenicity: FERRIC AMMONIUM CITRATE - Not listed by ACGIH, IARC, NIOSH, NTP, or OSHA. See actual entry in RTECS for complete information. Section 12 - ECOLOGICAL INFORMATION Other No information available. Section 13 - DISPOSAL CONSIDERATIONS Dispose of in a manner consistent with federal, state, and local regulations. Section 14 - TRANSPORT INFORMATION IATA Not regulated as a hazardous material. IMO Not regulated as a hazardous material. RID/ADR Not regulated as a hazardous material. Section 15 - REGULATORY INFORMATION European/International Regulations European Labeling in Accordance with EC Directives Hazard Symbols: Not available. Risk Phrases: Safety Phrases: S 24/25 Avoid contact with skin and eyes. WGK (Water Danger/Protection) CAS# 1185-57-5: No information available. United Kingdom Occupational Exposure Limits Canada CAS# 1185-57-5 is listed on Canada's DSL List. CAS# 1185-57-5 is not listed on Canada's Ingredient Disclosure List. Exposure Limits CAS# 1185-57-5: OEL-DENMARK:TWA 1 mg(Fe)/m3 JANUARY 1993 OEL-FINLAND:TWA 1 mg(Fe)/m3 JANUARY 1993 OEL-THE NETHERLANDS:TWA 1 mg(Fe)/m3 JANUARY 1993 OEL-SWITZERLAND:TWA 1 mg(Fe)/m3 JANUARY 1993 OEL-UNITED KINGDOM:TWA 1 mg(Fe)/m3;STEL 2 mg(Fe)/m3 JANUARY 1993 US FEDERAL TSCA CAS# 1185-57-5 is listed on the TSCA inventory. SECTION 16 - ADDITIONAL INFORMATION N/A |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | UN 9118 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | GE7540000 |
| HS Code | 2918150000 |
| HS Code | 2918150000 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2918150000. other salts and esters of citric acid. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. Supervision conditions:4ABXY(export license,certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outwardexport license(processing trade),export license(border small volume trade)). MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Iron overload causes oxidative stress and impaired insulin signaling in AML-12 hepatocytes.
Dig. Dis. Sci. 58(7) , 1899-908, (2013) Iron overload is associated with increased severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) including progression to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma.To identify potential... |
|
|
Effects of iron chelators, iron salts, and iron oxide nanoparticles on the proliferation and the iron content of oligodendroglial OLN-93 cells.
Neurochem. Res. 35(8) , 1259-68, (2010) The oligodendroglial cell line OLN-93 was used as model system to investigate the consequences of iron deprivation or iron excess on cell proliferation. Presence of ferric or ferrous iron chelators in... |
|
|
Heme controls ferroportin1 (FPN1) transcription involving Bach1, Nrf2 and a MARE/ARE sequence motif at position -7007 of the FPN1 promoter.
Gut 95 , 1261-8, (2010) Macrophages of the reticuloendothelial system play a key role in recycling iron from hemoglobin of senescent or damaged erythrocytes. Heme oxygenase 1 degrades the heme moiety and releases inorganic i... |
| Ferric |
| EINECS 214-686-6 |
| Iron(3+) 2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylate ammoniate (1:1:1) |
| Ferricammoniumcitrae |
| 1,2,3-Propanetricarboxylic acid, 2-hydroxy-, ammonium iron(3+) salt (1:1:1) |
| MFCD00013099 |
| Ammonium iron(III) citrate |
| Ammonium Ferric Citrate |
| Ammoniumironcitrate |
| IRON AMMONIUM CITRATE |
| Citric acid iron ammonium |
| Amonium Iron(III) Citrate Supplement |
| Ironandammoniumcit-rate |
| AmmoniumFerricCitrateUsp |

