sarcosine-methyl-d3
Modify Date: 2024-01-05 17:55:34
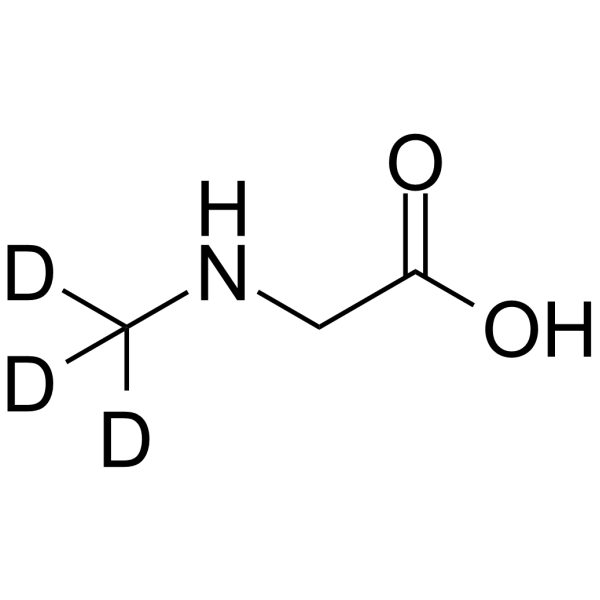
sarcosine-methyl-d3 structure
|
Common Name | sarcosine-methyl-d3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 118685-91-9 | Molecular Weight | 92.11170 | |
| Density | 1.13g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 195.1ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C3H4D3NO2 | Melting Point | 208ºC (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 71.8ºC | |
Use of sarcosine-methyl-d3Sarcosine-d3 (N-Methylglycine-d3) is the deuterium labeled Sarcosine. Sarcosine (N-Methylglycine), an endogenous amino acid, is a competitive glycine transporter type I (GlyT1) inhibitor and N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor co-agonist. Sarcosine increases the glycine concentration, resulting in an indirect potentiation of the NMDA receptor. Sarcosine is commonly used for the research of schizophrenia[1][2]. |
| Name | sarcosine-methyl-d3 |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Sarcosine-d3 (N-Methylglycine-d3) is the deuterium labeled Sarcosine. Sarcosine (N-Methylglycine), an endogenous amino acid, is a competitive glycine transporter type I (GlyT1) inhibitor and N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor co-agonist. Sarcosine increases the glycine concentration, resulting in an indirect potentiation of the NMDA receptor. Sarcosine is commonly used for the research of schizophrenia[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.13g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 195.1ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 208ºC (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C3H4D3NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 92.11170 |
| Flash Point | 71.8ºC |
| Exact Mass | 92.06650 |
| PSA | 49.33000 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.184mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.431 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|---|
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
~% 
sarcosine-methyl-d3 CAS#:118685-91-9 |
| Literature: MacKenzie; Abeles Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1956 , vol. 222, p. 145,148 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| n-Tridecyloxyessigsaeure-methylester |
| MFCD01075434 |
| N-trideuteriomethyl-glycine |
| N-Methyl-d3-glycine |