5,8,11,14-Icosatetraynoic acid
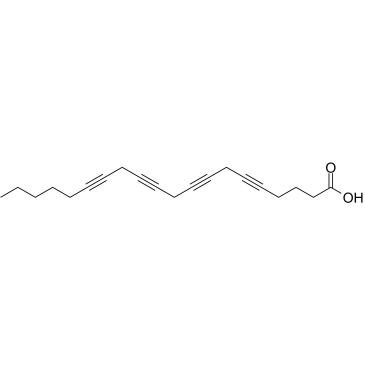
5,8,11,14-Icosatetraynoic acid structure
|
Common Name | 5,8,11,14-Icosatetraynoic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1191-85-1 | Molecular Weight | 296.403 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 490.3±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H24O2 | Melting Point | 79-81ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 226.6±23.4 °C | |
Use of 5,8,11,14-Icosatetraynoic acidEicosatetraynoic acid (ETYA) is a nonspecific inhibitor of cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase (ID50=8 μM and 4 μM, respectively)[1]. Eicosatetraynoic acid (ETYA) activates PPARα and PPARγ chimeras at 10 µM[2]. |
| Name | icosa-5,8,11,14-tetraynoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Eicosatetraynoic acid (ETYA) is a nonspecific inhibitor of cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase (ID50=8 μM and 4 μM, respectively)[1]. Eicosatetraynoic acid (ETYA) activates PPARα and PPARγ chimeras at 10 µM[2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
COX:8 μM (ID50) |
| References |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 490.3±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 79-81ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C20H24O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 296.403 |
| Flash Point | 226.6±23.4 °C |
| Exact Mass | 296.177643 |
| PSA | 37.30000 |
| LogP | 5.19 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.528 |
| InChIKey | MGLDCXPLYOWQRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CCCCCC#CCC#CCC#CCC#CCCCC(=O)O |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| HS Code | 2916190090 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 4 | |
| HS Code | 2916190090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2916190090 unsaturated acyclic monocarboxylic acids, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives。supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward)。VAT:17.0%。tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:6.5%。general tariff:30.0% |
|
Arachidonic acid induces brain endothelial cell apoptosis via p38-MAPK and intracellular calcium signaling.
Microvasc. Res. 98 , 145-58, (2015) Arachidonic acid (AA), a bioactive fatty acid whose levels increase during neuroinflammation, contributes to cerebral vascular damage and dysfunction. However, the mode of injury and underlying signal... |
|
|
High extracellular Ca2+ stimulates Ca2+-activated Cl- currents in frog parathyroid cells through the mediation of arachidonic acid cascade.
PLoS ONE 6(4) , e19158, (2011) Elevation of extracellular Ca(2+) concentration induces intracellular Ca(2+) signaling in parathyroid cells. The response is due to stimulation of the phospholipase C/Ca(2+) pathways, but the direct m... |
|
|
Reactive oxygen species mediate arachidonic acid-induced dilation in porcine coronary microvessels.
Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 285(6) , H2309-15, (2003) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) have been proposed to mediate vasodilation in the microcirculation. We investigated the role of ROS in arachidonic acid (AA)-induced coronary microvascular dilation. Porc... |
| Eicosa-5,8,11,14-tetrainsaeure |
| MFCD00036967 |
| 5,8,11,14-eicosatetrayonic acid |
| 5,8,11,14-Icosatetraynoic acid |
| 5,8,11,14-Eicosatetraynoic acid |
| ETYA |
| Icosa-5,8,11,14-tetraynoic acid |
| Octadehydroarachidonic acid |
| eicosatetraynoic acid |
 CAS#:102471-97-6
CAS#:102471-97-6 CAS#:35378-79-1
CAS#:35378-79-1 CAS#:34498-24-3
CAS#:34498-24-3 CAS#:35378-84-8
CAS#:35378-84-8 CAS#:18495-27-7
CAS#:18495-27-7 CAS#:53293-00-8
CAS#:53293-00-8 CAS#:628-71-7
CAS#:628-71-7 CAS#:14918-21-9
CAS#:14918-21-9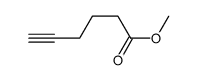 CAS#:77758-51-1
CAS#:77758-51-1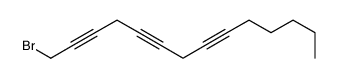 CAS#:34498-26-5
CAS#:34498-26-5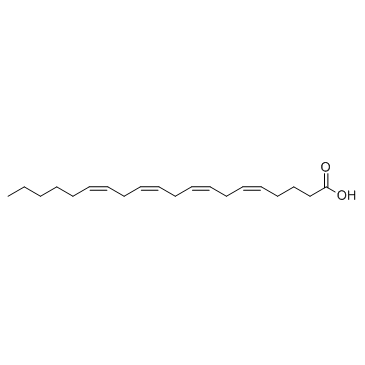 CAS#:506-32-1
CAS#:506-32-1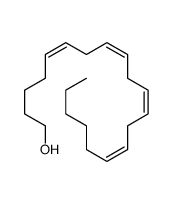 CAS#:13487-46-2
CAS#:13487-46-2 CAS#:2566-89-4
CAS#:2566-89-4![ARACHIDONIC ACID, [5,6,8,9,11,12,14,15-3H(N)]- structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/375/66753-05-7.png) CAS#:66753-05-7
CAS#:66753-05-7