L-Azidohomoalanine
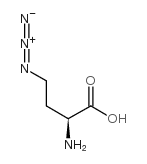
L-Azidohomoalanine structure
|
Common Name | L-Azidohomoalanine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 120042-14-0 | Molecular Weight | 144.13200 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H8N4O2 | Melting Point | 220-223ºC | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of L-AzidohomoalanineL-Azidohomoalanine is an alkyl chain-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs[1]. |
| Name | (2S)-2-amino-4-azidobutanoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | L-Azidohomoalanine is an alkyl chain-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Alkyl-Chain |
| In Vitro | PROTACs contain two different ligands connected by a linker; one is a ligand for an E3 ubiquitin ligase and the other is for the target protein. PROTACs exploit the intracellular ubiquitin-proteasome system to selectively degrade target proteins[1]. |
| References |
| Melting Point | 220-223ºC |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C4H8N4O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 144.13200 |
| Exact Mass | 144.06500 |
| PSA | 113.07000 |
| LogP | 0.25176 |
|
~98% 
L-Azidohomoalanine CAS#:120042-14-0 |
| Literature: Roth, Stefanie; Thomas, Neil R. Synlett, 2010 , # 4 art. no. D28009ST, p. 607 - 609 |
|
~% 
L-Azidohomoalanine CAS#:120042-14-0 |
| Literature: European Journal of Organic Chemistry, , # 31 p. 5308 - 5314 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| 4-Azido-homoalanine |
| 2(S)-Amino-4-azido-butanoic Acid |
| azidohomoalanine |
| Butanoic acid,2-amino-4-azido-,(2S) |
| AmbotzHAA5730 |
| L-Azidohomoalanine |
| 4-Azido-L-2-aminobutyrate |
| azodohomoalanine |
| L-4-azido-2-aminobutanoic acid |

