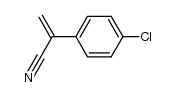
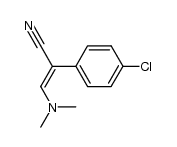
Saclofen
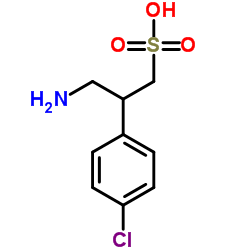
Saclofen structure
|
Common Name | Saclofen | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 125464-42-8 | Molecular Weight | 249.714 | |
| Density | 1.437±0.06 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H12ClNO3S | Melting Point | 310-315 ºC | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of SaclofenSaclofen is a competitive antagonist of the GABAB receptor with an IC50 of 7.8 μM. Saclofen can be used to determine the functional roles for the GABAB receptor as a mediator of slow inhibitory postsynaptic potentials in the brain[1]. |
| Name | 3-Amino-2-(4-chlorophenyl)propane-1-sulfonic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Saclofen is a competitive antagonist of the GABAB receptor with an IC50 of 7.8 μM. Saclofen can be used to determine the functional roles for the GABAB receptor as a mediator of slow inhibitory postsynaptic potentials in the brain[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.437±0.06 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 310-315 ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C9H12ClNO3S |
| Molecular Weight | 249.714 |
| Exact Mass | 249.022644 |
| PSA | 88.77000 |
| LogP | 0.03 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.600 |
| Storage condition | Store at RT |
| Water Solubility | Slightly soluble (7.5 g/L) (25 ºC) |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2921499090 |
|
~58% 
Saclofen CAS#:125464-42-8 |
| Literature: Li; Howson; Dolle Synthesis, 1991 , # 3 p. 244 - 244 |
|
~% 
Saclofen CAS#:125464-42-8 |
| Literature: Synthesis, , # 3 p. 244 - 244 |
|
~% 
Saclofen CAS#:125464-42-8 |
| Literature: Synthesis, , # 3 p. 244 - 244 |
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| HS Code | 2921499090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2921499090 other aromatic monoamines and their derivatives; salts thereof VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Opioid receptor-dependent sex differences in synaptic plasticity in the hippocampal mossy fiber pathway of the adult rat.
J. Neurosci. 35(4) , 1723-38, (2015) The mossy fiber (MF) pathway is critical to hippocampal function and influenced by gonadal hormones. Physiological data are limited, so we asked whether basal transmission and long-term potentiation (... |
|
|
Spinal segmental and supraspinal mechanisms underlying the pain-relieving effects of spinal cord stimulation: an experimental study in a rat model of neuropathy.
Neuroscience 215 , 196-208, (2012) Spinal cord stimulation (SCS) may alleviate certain forms of neuropathic pain; its mechanisms of action are, however, not fully understood. Previous studies have mainly been focused onto segmental spi... |
|
|
GABA-induced uncoupling of GABA/benzodiazepine site interactions is associated with increased phosphorylation of the GABAA receptor.
J. Neurosci. Res. 92(8) , 1054-61, (2014) The use-dependent regulation of the GABAA receptor occurs under physiological, pathological, and pharmacological conditions. Tolerance induced by prolonged administration of benzodiazepines is associa... |
| Saclofen |
| 3-Amino-2-(4-chlorophenyl)propane-1-sulfonic acid |
| UNII:LRZ36BCQ1Y |
| Benzeneethanesulfonic acid, β-(aminomethyl)-4-chloro- |
| MFCD00216817 |
| 3-Amino-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-propanesulfonic acid |
| beta-(Aminomethyl)-4-chlorobenzeneethanesulfonic acid |