goralatide
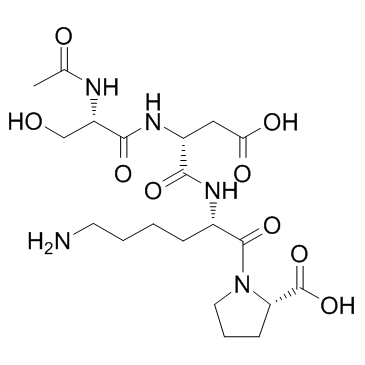
goralatide structure
|
Common Name | goralatide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 127103-11-1 | Molecular Weight | 487.504 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 992.0±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H33N5O9 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 553.7±34.3 °C | |
Use of goralatideN-Acetyl-Ser-Asp-Lys-Pro is a natural and specific substrate for the N-terminal site of ACE. |
| Name | 1-[2-[[2-[(2-acetamido-3-hydroxypropanoyl)amino]-3-carboxypropanoyl]amino]-6-aminohexanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | N-Acetyl-Ser-Asp-Lys-Pro is a natural and specific substrate for the N-terminal site of ACE. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | N-Acetyl-Ser-Asp-Lys-Pro is an endogenous tetrapeptide secreted by bone marrow and is ubiquitously found in plasma and various tissues. N-Acetyl-Ser-Asp-Lys-Pro is degraded specifically by ACE, and its plasma level rises substantially during ACE inhibitor therapy. N-Acetyl-Ser-Asp-Lys-Pro inhibits the proliferation of isolated cardiac fibroblasts but significantly stimulates the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Flow cytometry of rat cardiac fibroblasts treated with N-Acetyl-Ser-Asp-Lys-Pro shows significant inhibition of the progression of cells from G0/G1 phase to S phase of the cell cycle. In cardiac fibroblasts transfected with a Smad-sensitive luciferase reporter construct, N-Acetyl-Ser-Asp-Lys-Pro decreases luciferase activity by 55%. Moreover, phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of Smad2 is decreased in cardiac fibroblasts treated with N-Acetyl-Ser-Asp-Lys-Pro[1]. N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline is a negative regulator of hematopoietic stem cell proliferation. N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline is involved in the control of hematopoietic stem cell proliferation by preventing their recruitment into S-phase. N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline appears to exert this function by blocking the action of a stem cell-specific proliferation stimulator and acts selectively on quiescent progenitors[2]. N-Acetyl-Ser-Asp-Lys-Pro inhibits collagenase expression and activation is associated with increased expression of TIMP-1 and TIMP-2. N-Acetyl-Ser-Asp-Lys-Pro does not alter collagenase or gelatinase activity in cardiac fibroblasts under basal conditions, but blunts the IL-1β-induced increase in total collagenase activity. Similarly, N-Acetyl-Ser-Asp-Lys-Pro normalizes the IL-1β-mediated increase in MMP-2 and MMP-9 activities and MMP-13 expression[3]. |
| In Vivo | N-Acetyl-Ser-Asp-Lys-Pro prevents hypertension-induced inflammatory cell infiltration, collagen deposition, nephrin downregulation and albuminuria, which could lead to renoprotection in hypertensive mice[4]. |
| Kinase Assay | The kinetics of N-Acetyl-Ser-Asp-Lys-Pro hydrolysis are determined by incubating enzymes (0.4 nM wild-type ACE, 0.3 nM ACE K959 963, and 9 nM ACE K361 365) with N-Acetyl-Ser-Asp-Lys-Pro over a concentration range of 0.35-40 μM, added to [3H]N-Acetyl-Ser-Asp-Lys-Pro (5 μCi). The reaction is stopped by freezing on dry ice, and samples are then analyzed[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice: 16-week-old C57BL/6J mice are treated with either placebo, DCOA (10 mg/10 g body weight subcutaneous) and 1% sodium chloride with 0.2% potassium chloride in drinking water (DOCA-salt) or DOCA-salt with Ac-SDKP (800 μg/kg per day) for 12 weeks. Bloof pressure, urine albumin, glomerular matrix, renal collagen content, monocyte/macrophage infiltration and glomerular nephrin expression are measured[4]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 992.0±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C20H33N5O9 |
| Molecular Weight | 487.504 |
| Flash Point | 553.7±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 487.227814 |
| PSA | 238.93000 |
| LogP | -1.91 |
| Appearance of Characters | Solid | White to off-white |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.565 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water at 2mg/ml |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|---|
|
~% 
goralatide CAS#:127103-11-1 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 33, # 8 p. 2122 - 2127 |
|
~% 
goralatide CAS#:127103-11-1 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 33, # 8 p. 2122 - 2127 |
|
~% 
goralatide CAS#:127103-11-1 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 33, # 8 p. 2122 - 2127 |
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| goralatide |
| L-Proline, N-acetyl-L-seryl-L-α-aspartyl-L-lysyl- |
| Acetyl-Ser-Asp-Lys-Pro |
| NAcSerDAspLysPro |
| N-Acetyl-L-seryl-L-α-aspartyl-L-lysyl-L-proline |
| MFCD00133611 |
| 1-(N2-(N-(N-Acetyl-L-seryl)-L-a-aspartyl)-L-lysyl)-L-proline |
| Ac-Ser-Asp-Lys-Pro-OH |
| Thymosin β4 (1-4) |
| N-Acetyl-Ser-Asp-Lys-Pro |