Antileukinate
Modify Date: 2025-08-25 15:34:36
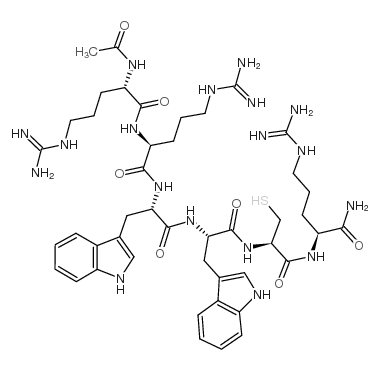
Antileukinate structure
|
Common Name | Antileukinate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 138559-60-1 | Molecular Weight | 1003.19000 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C45H66N18O7S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of AntileukinateAntileukinate, a hexapeptide, is a potent inhibitor of CXC-chemokine receptor (CXCR). Antileukinate inhibits neutrophil chemotaxis and activation. Antileukinate can be used for the research of acute inflammation and injury[1][2][3]. |
| Name | IL-8 Inhibitor |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Antileukinate, a hexapeptide, is a potent inhibitor of CXC-chemokine receptor (CXCR). Antileukinate inhibits neutrophil chemotaxis and activation. Antileukinate can be used for the research of acute inflammation and injury[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Antileukinate inhibits the binding of human eotaxin to human eosinophils with an IC50 of 8.2 μM[2]. Antileukinate (10 μM, 100 μM) significantly suppresses eosinophil chemotaxis to human eotaxin[2]. |
| In Vivo | Antileukinate (52.63 mg/kg; s.c.) protectes mice against acute pancreatitis and associated lung injury[1]. Antileukinate (5mg/kg; s.c.) inhibits the interaction between murine eotaxin and murine eosinophil[2]. Animal Model: Swiss mice(20-25g)[1] Dosage: 52.63 mg/kg Administration: Subcutaneous injection Result: Reduced pancreatic edema induced by Caerulein (50 μg/kg). |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C45H66N18O7S |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 1003.19000 |
| Exact Mass | 1002.51000 |
| PSA | 473.77000 |
| LogP | 4.18650 |
| InChIKey | FVRBFNYUBYTVIQ-NGTAMTFRSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(=O)NC(CCCN=C(N)N)C(=O)NC(CCCN=C(N)N)C(=O)NC(Cc1c[nH]c2ccccc12)C(=O)NC(Cc1c[nH]c2ccccc12)C(=O)NC(CS)C(=O)NC(CCCN=C(N)N)C(N)=O |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|
| ac-rrwwcr-nh2 |
| ac-arg-arg-trp-trp-cys-arg-nh2 |

