Nogalamycin
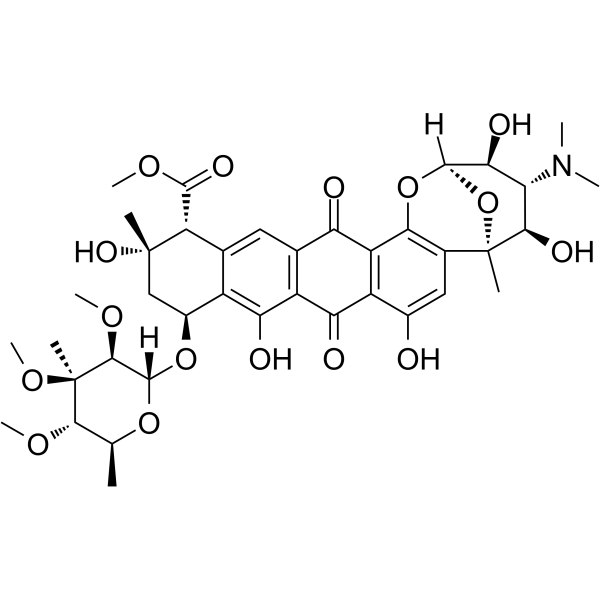
Nogalamycin structure
|
Common Name | Nogalamycin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1404-15-5 | Molecular Weight | 787.80 | |
| Density | 1.49g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 899.9ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C39H49NO16 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 498.1ºC | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of NogalamycinNogalamycin is an anthracyclinone antibiotic. Nogalamycin is a potent antibiotic against Gram-positive bacteria, also has cytotoxicity against certain tumor cells. Nogalamycin is produced by Streptomyces nogalater var. Nogalater. Nogalamycin selectively inhibits RNA synthesis after binding to DNA template. Nogalamycin can be used for researching anticancer[1][2]. |
| Name | nogalamycin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Nogalamycin is an anthracyclinone antibiotic. Nogalamycin is a potent antibiotic against Gram-positive bacteria, also has cytotoxicity against certain tumor cells. Nogalamycin is produced by Streptomyces nogalater var. Nogalater. Nogalamycin selectively inhibits RNA synthesis after binding to DNA template. Nogalamycin can be used for researching anticancer[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
RNA Synthesis[2] |
| In Vitro | Nogalamycin (0-10 μg/ml; 2 hours) exhibits lethality against CHO, L1210 and B16 with LD50s of 2.74 μg/ml, 0.25 μg/ml and 0.15 μg/ml[1]. Cell Cytotoxicity Assay Cell Line: CHO, L1210 and B16 cells[1] Concentration: 0-10 μg/ml Incubation Time: 2 hours Result: Exhibited lethality against CHO, L1210 and B16 with LD50s of 2.74 μg/ml, 0.25 μg/ml and 0.15 μg/ml. |
| In Vivo | Nogalamycin (0-1000 mug/kg; IP) can regress chemically-induced fibrosarcoma tumors and tumors of spontaneous origin in rats[3]. Animal Model: Rats[1] Dosage: 0-1000 mug/kg Administration: IP Result: Regressed chemically-induced fibrosarcoma tumors and tumors of spontaneous origin in rats, and the most effective concentration was 556 mug/kg. |
| References |
| Density | 1.49g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 899.9ºC at 760mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C39H49NO16 |
| Molecular Weight | 787.80 |
| Flash Point | 498.1ºC |
| Exact Mass | 787.30500 |
| PSA | 229.44000 |
| LogP | 1.13800 |
| Vapour Pressure | 7.49E-35mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.648 |
| InChIKey | KGTDRFCXGRULNK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | COC(=O)C1c2cc3c(c(O)c2C(OC2OC(C)C(OC)C(C)(OC)C2OC)CC1(C)O)C(=O)c1c(O)cc2c(c1C3=O)OC1OC2(C)C(O)C(N(C)C)C1O |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H312-H332-H350-H360 |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P280-P308 + P313 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T: Toxic; |
| Risk Phrases | 45-46-61-20/21/22 |
| Safety Phrases | 53-22-36/37/39-45 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| RTECS | RA4550000 |
|
Kinetic characterization of small DNA-binding molecules interacting with a DNA strand on a quartz crystal microbalance.
Anal. Biochem. 492 , 34-42, (2015) Quantitative studies of the binding of various DNA-binding antibiotics with dsDNA are useful for drug design, not only for effective antibiotics, but also for antitumor drugs. We studied the binding k... |
|
|
The intercalation of DNA double helices with doxorubicin and nogalamycin.
J. Mol. Graph. Model. 26(1) , 14-9, (2007) A variety of molecules bind to DNA in its major and minor grooves, and some, like the anthraquinoids, are known to form intercalates in which these molecules are inserted directly into the double heli... |
|
|
Engineering anthracycline biosynthesis toward angucyclines.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 47(4) , 1291-6, (2003) The biosynthesis pathways of two anthracyclines, nogalamycin and aclacinomycin, were directed toward angucyclines by using an angucycline-specific cyclase, pgaF, isolated from a silent antibiotic bios... |
| antibiotic205t3 |
| nogalomycin |
| NOGALAMYCIN |
| NOGALAMYCIN,STREPTOMYCES NOGALATER |