Neomycin sulfate
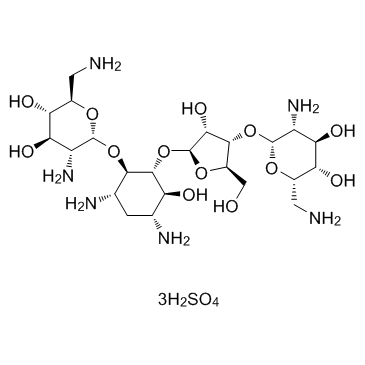
Neomycin sulfate structure
|
Common Name | Neomycin sulfate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1405-10-3 | Molecular Weight | 908.88 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 1046.1ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C23H52N6O25S3 | Melting Point | >187°C (dec.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 586.5ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Neomycin sulfateNeomycin sulfate is an aminoglycoside antibiotic used for preventing or treating bacterial infections. |
| Name | Fradiomycin Sulfate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Neomycin sulfate is an aminoglycoside antibiotic used for preventing or treating bacterial infections. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Neomycin inhibits thrombin-stimulated release of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3), by selectively binding PIP2, but does not inhibit 32P incorporation into PI or initiation of DNA synthesis[1]. Neomycin (10 μM-1 mM) induces considerable release of [3H]arachidonic acid from phosphatidylinositol, phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine in saponin-permeabilized human platelets prelabeled with [3H]arachidonic acid. Moreover, neomycin enhances arachidonic acid release induced by thrombin. Addition of neomycin (100 μM) to 45Ca2+-preloaded platelets elicits 45Ca2+ mobilizatioin from intracellular stores[2]. Neomycin (0-10 mM) inhibits guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate-stimulated PLD activity in digitonin-permeabilized NG108-15 cells in a concentration-dependent manner (50% inhibition at 100 μM). Neomycin similarly inhibits PLD activity present in rat brain membranes and assayed in vitro with [3H]phosphatidylcholine as substrate (50% inhibition at 65 μM)[3]. Neomycin (5 mM) causes reversible reductions in the level of intracellular Ca2+, but PtdIns(4,5)P2 is not required for the channel activity[4]. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 1046.1ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | >187°C (dec.) |
| Molecular Formula | C23H52N6O25S3 |
| Molecular Weight | 908.88 |
| Flash Point | 586.5ºC |
| PSA | 436.09000 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 56 ° (C=10, H2O) |
| InChIKey | KWBUARAINLGYMG-BNAHOEIWSA-N |
| SMILES | NCC1OC(OC2C(CO)OC(OC3C(O)C(N)CC(N)C3OC3OC(CN)C(O)C(O)C3N)C2O)C(N)C(O)C1O.O=S(=O)(O)O.O=S(=O)(O)O.O=S(=O)(O)O |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | H2O: 50 mg/mL As a stock solution. Stock solutions should be filter sterilized and stored at 2-8°C. Stable at 37°C for 5 days. |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H317-H334 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P342 + P311 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Phrases | R42/43 |
| Safety Phrases | 23-36/37-45-22-36-24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | QP4375000 |
| HS Code | 2941909000 |
| HS Code | 2941909000 |
|---|
|
Effect of selective decontamination on antimicrobial resistance in intensive care units: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Lancet Infect. Dis. 13(4) , 328-41, (2013) Many meta-analyses have shown reductions in infection rates and mortality associated with the use of selective digestive decontamination (SDD) or selective oropharyngeal decontamination (SOD) in inten... |
|
|
Clearance of nasal Staphylococcus aureus colonization with triple antibiotic ointment.
Journal. of. Drugs in. Dermatology. 11(12) , 1490-2, (2012) The prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus colonization of healthcare workers is reported at 30%, with colonization rates for methicillin-resistant S aureus (MRSA) reported between 2.0% and 8.5% among in... |
|
|
Acute otitis externa: an update.
Am. Fam. Physician 86(11) , 1055-61, (2012) Acute otitis externa is a common condition involving inflammation of the ear canal. The acute form is caused primarily by bacterial infection, with Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus the... |
| Neomycin Sulfate |
| FradioMycin Sulfate |
| Neomycin Sulphate |
| Neomycin trisulfate salt hydrate |
| EINECS 215-773-1 |
| MFCD00037007 |

