Sacubitrilat
Modify Date: 2025-09-03 10:11:38
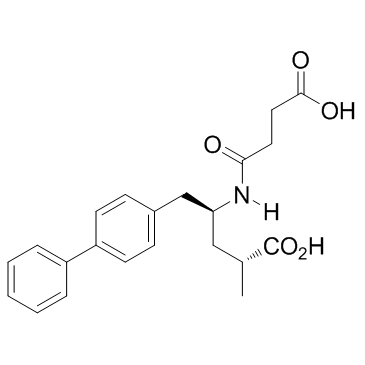
Sacubitrilat structure
|
Common Name | Sacubitrilat | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 149709-44-4 | Molecular Weight | 383.43800 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C22H25NO5 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of SacubitrilatSacubitrilat is an active neprilysin (NEP) inhibitor. |
| Name | (2R,4S)-4-(3-carboxypropanoylamino)-2-methyl-5-(4-phenylphenyl)pentanoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Sacubitrilat is an active neprilysin (NEP) inhibitor. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Neprilysin[1] |
| In Vitro | Sacubitrilat (LBQ657) is a single diastereomer with specific stereocenters. Sacubitrilat is bound to the active site of NEP by an intricate network of interactions that involves all functional groups of the compound giving rise to the high inhibitory potency of 5 nM[1]. |
| In Vivo | Pharmacokinetics of Sacubitril, Sacubitrilat (LBQ657), and valsartan following the administration of single oral doses of LCZ696 400 or 1200 mg under fasting condition are summarized. The mean plasma concentrations of Sacubitril increases rapidly with a median Tmax of 0.52 h for the 400 mg dose and 1.05 h for the 1200 mg dose, followed by Sacubitrilat, with the corresponding Tmax values of 2.07 and 3.05 h, respectively. The median Tmax for valsartan is 2.07 h for both the LCZ696 400 mg and 1200 mg doses. The Cmax of Sacubitrilat shows a dose proportional increase, while the Cmax of Sacubitril and Valsartan shows less than proportional increases between the doses. The arithmetic mean AUC0-24 h and AUClast for Sacubitril and Sacubitrilat increases approximately dose proportionally, but shows less than dose proportional increase for Valsartan[2]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C22H25NO5 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 383.43800 |
| Exact Mass | 383.17300 |
| PSA | 107.19000 |
| LogP | 4.19680 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
| (2R,4S)-5-(Biphenyl-4-yl)-4-((3-carboxypropionyl)amino)-2-methylpentanoic acid |
| LBQ657 |
| UNII-SPI5PBF81S |
| Sacubitrilat |