Isolithocholic Acid
Modify Date: 2024-01-11 23:11:20
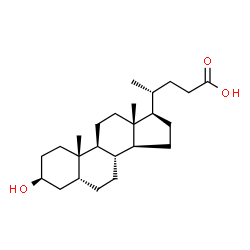
Isolithocholic Acid structure
|
Common Name | Isolithocholic Acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1534-35-6 | Molecular Weight | 376.57 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 511.0±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C24H40O3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 276.9±19.1 °C | |
Use of Isolithocholic AcidIsolithocholic acid (β-Lithocholic acid) is an isomer of Lithocholic acid. Isolithocholic acid, a bile acid, is formed by microbial metabolism of Lithocholic acid or Lithocholic acid 3α-sulfate[1][2]. |
| Name | Isolithocholic Acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Isolithocholic acid (β-Lithocholic acid) is an isomer of Lithocholic acid. Isolithocholic acid, a bile acid, is formed by microbial metabolism of Lithocholic acid or Lithocholic acid 3α-sulfate[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Microbial Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Isolithocholic acid at 0.01 % does not inhibit spore germination and outgrowth of CF5 and M120, but it significantly inhibits at the higher concentration (0.1 %). Isolithocholic acid (0.00003 %) prevents growth of CD196, M68, CF5, 630, and BI9 and significant decreases strains CF5, BI9, M120, and 630 in toxin activity. Isolithocholic acid (0.0003 %) makes that all strains displays a significant decrease in toxin activity, except for R20291 and M120[3]. |
| In Vivo | The levels of fecal Isolithocholic acid shows obvious decreases from day 28 onward in the high fat diet (HFD) group compared with rats fed a normal diet[4]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 511.0±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C24H40O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 376.57 |
| Flash Point | 276.9±19.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 376.297760 |
| LogP | 6.70 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.528 |
| Storage condition | 2-8 °C |
| 3b-Hydroxy-5b-cholan-24-oic acid |
| 3b-Lithocholic acid |
| 3β-Hydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic Acid |
| Cholan-24-oic acid, 3-hydroxy-, (3β,5β)- |
| Isolithocholic acid |
| (3β,5β)-3-Hydroxycholan-24-oic acid |
| (3β,5β,20R)-3-Hydroxycholan-24-oic acid |
| (3β,5β)-3-hydroxy-cholan-24-oic acid |
| Cholan-24-oic acid, 3-hydroxy-, (3β,5β,20R)- |
| MFCD00271385 |