Chlortoluron
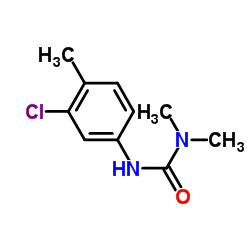
Chlortoluron structure
|
Common Name | Chlortoluron | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 15545-48-9 | Molecular Weight | 212.676 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 345.9±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H13ClN2O | Melting Point | 147-148ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 163.0±30.7 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of ChlortoluronChlorotoluron (Chlortoluron) is a substituted phenylurea herbicide, is widely used for selective weed control in cereals crops and is an environmental pollutant[1]. |
| Name | chlorotoluron |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Chlorotoluron (Chlortoluron) is a substituted phenylurea herbicide, is widely used for selective weed control in cereals crops and is an environmental pollutant[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 345.9±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 147-148ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C10H13ClN2O |
| Molecular Weight | 212.676 |
| Flash Point | 163.0±30.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 212.071640 |
| PSA | 32.34000 |
| LogP | 2.62 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.541 |
| InChIKey | JXCGFZXSOMJFOA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | Cc1ccc(NC(=O)N(C)C)cc1Cl |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS08, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H351-H361d-H410 |
| Precautionary Statements | P273-P281-P501 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful;N:Dangerousfortheenvironment; |
| Risk Phrases | R40;R50/53;R63 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37-S46-S60-S61-S16 |
| RIDADR | UN 3077 |
| RTECS | YS7230000 |
| HS Code | 2924299035 |
|
~90% 
Chlortoluron CAS#:15545-48-9 |
| Literature: Rauf, Waqar; Thompson, Amber L.; Brown, John M. Chemical Communications, 2009 , # 26 p. 3874 - 3876 |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2924299035 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924299035 2-chlorobenzaldehyde。supervision conditions:s(import or export registration certificate for pesticides)。VAT:17.0%。tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tarrif:6.5%。general tariff:30.0% |
|
Assessing the potential for algae and macrophytes to degrade crop protection products in aquatic ecosystems.
Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 30(3) , 622-31, (2011) Rates of pesticide degradation in aquatic ecosystems often differ between those observed within laboratory studies and field trials. Under field conditions, a number of additional processes may well h... |
|
|
Polymer monolith microextraction using poly(butyl methacrylate-co-1,6-hexanediol ethoxylate diacrylate) monolithic sorbent for determination of phenylurea herbicides in water samples.
Talanta 147 , 199-206, (2015) In this study, recently developed 1,6-hexanediol ethoxylate diacrylate (HEDA)-based polymeric monoliths were utilized as sorbents for efficient extraction of phenylurea herbicides (PUHs) from water sa... |
|
|
Analysis of trace levels of pesticides in rainwater by SPME and GC-tandem mass spectrometry after derivatisation with PFBBr.
Anal. Bioanal. Chem 387(1) , 359-68, (2007) Solid-phase microextraction (SPME) was used for the analysis of some pesticides (bromoxynil, chlorotoluron, diuron, isoproturon, 2,4-MCPA, MCPP and 2,4-D) in rainwater after derivatisation with PFBBr ... |
| Chlorotoluron |
| Methanol, 1-[(3-chloro-4-methylphenyl)imino]-1-(dimethylamino)-, (E)- |
| Urea, N'-(3-chloro-4-methylphenyl)-N,N-dimethyl- |
| N’-(3-chloro-4-methylphenyl)-N,N-dimethylurea |
| 3-(3-Chloro-4-methylphenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea |
| MFCD00018275 |
| Chlortoluron |
| 3-(3-chloro-p-tolyl)-1,1-dimethylurea |
| EINECS 239-592-2 |
| 3-(3-Chloro-4-methyl)-1,1-dimethylurea |
| N'-(3-Chloro-4-methylphenyl)-N,N-dimethylcarbamimidic acid |
 CAS#:74-89-5
CAS#:74-89-5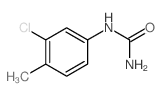 CAS#:13142-64-8
CAS#:13142-64-8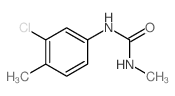 CAS#:22175-22-0
CAS#:22175-22-0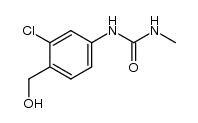 CAS#:59587-00-7
CAS#:59587-00-7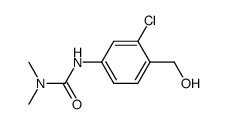 CAS#:59587-03-0
CAS#:59587-03-0![2-Chloro-4-[(dimethylcarbamoyl)amino]benzoic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/421/59587-01-8.png) CAS#:59587-01-8
CAS#:59587-01-8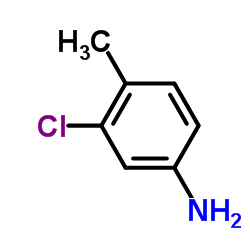 CAS#:95-74-9
CAS#:95-74-9 CAS#:7260-94-8
CAS#:7260-94-8
