Baceridin
Modify Date: 2025-12-06 19:01:04
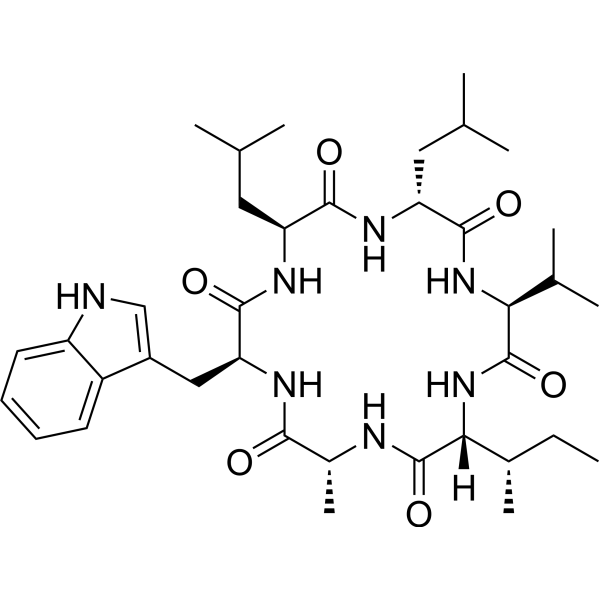
Baceridin structure
|
Common Name | Baceridin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1622872-91-6 | Molecular Weight | 695.9 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C37H57N7O6 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of BaceridinBaceridin is a proteasome inhibitor and a cyclic hexapeptide. Baceridin can be isolated from the culture medium of Epiphytic Bacillus. Baceridin can inhibit cell cycle progression and induce tumor cell apoptosis through a p53-independent pathway. Baceridin can be used in cancer research[1]. |
| Name | Baceridin |
|---|
| Description | Baceridin is a proteasome inhibitor and a cyclic hexapeptide. Baceridin can be isolated from the culture medium of Epiphytic Bacillus. Baceridin can inhibit cell cycle progression and induce tumor cell apoptosis through a p53-independent pathway. Baceridin can be used in cancer research[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C37H57N7O6 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 695.9 |
| InChIKey | KULVZQUHMGDNPX-FNDSQMSDSA-N |
| SMILES | CCC(C)C1NC(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(Cc2c[nH]c3ccccc23)NC(=O)C(C)NC1=O |