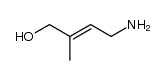
trans-Zeatin

trans-Zeatin structure
|
Common Name | trans-Zeatin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1637-39-4 | Molecular Weight | 219.243 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 395.0±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H13N5O | Melting Point | 207 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 192.7±30.7 °C | |
Use of trans-Zeatintrans-Zeatin is a plant cytokinin, which plays an important role in cell growth, differentiation, and division; trans-Zeatin also inhibits UV-induced MEK/ERK activation. |
| Name | trans-zeatin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | trans-Zeatin is a plant cytokinin, which plays an important role in cell growth, differentiation, and division; trans-Zeatin also inhibits UV-induced MEK/ERK activation. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
MEK ERK |
| In Vitro | trans-Zeatin is a plant cytokinin, which plays an important role in cell growth, differentiation, and division[1]. trans-Zeatin (20, 40 or 80 μM) inhibits UV-induced MEK/ERK activation, upregulates AQP3 in a time- and dose-dependent manner, and attenuates UV induced loss of AQP3 in keratinocytes (HaCaT cells). UV-induced AQP3 downregulation is blocked by MEK/ERK inhibitors. Trans-Zeatin (80 μM) attenuates UV-induced downregulation of wound healing and water permeability in HaCaT cells[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 395.0±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 207 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C10H13N5O |
| Molecular Weight | 219.243 |
| Flash Point | 192.7±30.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 219.112015 |
| PSA | 86.72000 |
| LogP | -1.02 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.684 |
| InChIKey | UZKQTCBAMSWPJD-FARCUNLSSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(=CCNc1ncnc2nc[nH]c12)CO |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Water Solubility | H2O: soluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATAMUTATION DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | EM9506000 |
|
~78% 
trans-Zeatin CAS#:1637-39-4 |
| Literature: Shadid, Belal; Plas, H. C. van der; Boesten, W. H. J.; Kamphuis, J.; Meijer, E. M.; Schoemaker, H. E. Tetrahedron, 1990 , vol. 46, # 3 p. 913 - 920 |
|
~% 
trans-Zeatin CAS#:1637-39-4 |
| Literature: Tetrahedron, , vol. 46, # 3 p. 913 - 920 |
|
~% 
trans-Zeatin CAS#:1637-39-4 |
| Literature: Organic Preparations and Procedures International, , vol. 29, # 5 p. 549 - 560 |
|
~% 
trans-Zeatin CAS#:1637-39-4 |
| Literature: Organic Preparations and Procedures International, , vol. 29, # 5 p. 549 - 560 |
|
~% 
trans-Zeatin CAS#:1637-39-4 |
| Literature: Organic Preparations and Procedures International, , vol. 29, # 5 p. 549 - 560 |
|
~% 
trans-Zeatin CAS#:1637-39-4 |
| Literature: Biochemical Journal, , vol. 458, # 2 p. 225 - 237 |
|
Silicon induces resistance to the brown spot fungus Cochliobolus miyabeanus by preventing the pathogen from hijacking the rice ethylene pathway.
New Phytol. 206(2) , 761-73, (2015) Although numerous studies have shown the ability of silicon (Si) to mitigate a wide variety of abiotic and biotic stresses, relatively little is known about the underlying mechanism(s). Here, we have ... |
|
|
High-internal-phase-emulsion polymeric monolith coupled with liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry for enrichment and sensitive detection of trace cytokinins in plant samples.
Anal. Bioanal. Chem 407 , 6071-9, (2015) High-internal-phase-emulsion polymers (polyHIPEs) show great promise as solid-phase-extraction (SPE) materials because of the tremendous porosity and highly interconnected framework afforded by the hi... |
|
|
Physiological response to drought in radiata pine: phytohormone implication at leaf level.
Tree Physiol. 32(4) , 435-49, (2012) Pinus radiata D. Don is one of the most abundant species in the north of Spain. Knowledge of drought response mechanisms is essential to guarantee plantation survival under reduced water supply as pre... |
| (2z)-2-methyl-4-(9h-purin-6-ylamino)but-2-en-1-ol |
| 2-Buten-1-ol, 2-methyl-4-(1H-purin-6-ylamino)-, (2E)- |
| cis-zeatin |
| trans-Zeatin (synthetic) |
| (2E)-2-Methyl-4-(1H-purin-6-ylamino)-2-buten-1-ol |
| 2-Buten-1-ol, 2-methyl-4-(3H-purin-6-ylamino)-, (2Z)- |
| (E)-2-methyl-4-(7H-purin-6-ylamino)but-2-en-1-ol |
| oxyenadenine |
| (2E)-2-methyl-4-(7H-purin-6-ylamino)but-2-en-1-ol |
| ZEATIN TRANS ISOMER |
| (2Z)-2-Methyl-4-(3H-purin-6-ylamino)-2-buten-1-ol |
| 2-Buten-1-ol, 2-methyl-4-(3H-purin-6-ylamino)-, (2E)- |
| 6-(4-Hydroxy-3-methyl-2-butenylamino)purine |
| (E)-zeatin |
| (2E)-2-Methyl-4-(3H-purin-6-ylamino)-2-buten-1-ol |
| MFCD00213654 |
| (2E)-2-Methyl-4-(1H-purin-6-ylamino)but-2-en-1-ol |
| trans-Zeatin |
| (2E)-2-Methyl-4-(9H-purin-6-ylamino)but-2-en-1-ol |
| 2-Buten-1-ol, 2-methyl-4-(purin-6-ylamino)-, (E)- |
| N6-(4-Hydroxy-3-methyl-2-buten-1-yl)adenine |
| Zeatin |
| 6-(4-Hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enylamino)purine (N6-(4-Hydroxy-3-methyl-2-buten-1-yl)adenine |
| Zeatine |
| (2Z)-2-Methyl-4-(1H-purin-6-ylamino)-2-buten-1-ol |
| TRANS ISOMER-ZEATIN |
| ZEATINRESEARCH GRADE |
| 2-Buten-1-ol, 2-methyl-4-(7H-purin-6-ylamino)-, (2Z)- |
| 6-(4-Hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enylamino)purine |
| 2-Buten-1-ol, 2-methyl-4-(1H-purin-6-ylamino)-, (E)- |
| ZEATIN,CRYSTALLIZED |


![4-[tert-butyl(dimethyl)silyl]oxy-3-methylbut-2-enenitrile structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/477/78843-79-5.png)

 CAS#:55866-24-5
CAS#:55866-24-5
