6-(γ,γ-Dimethylallylamino)purine-d6
Modify Date: 2024-04-06 18:25:14
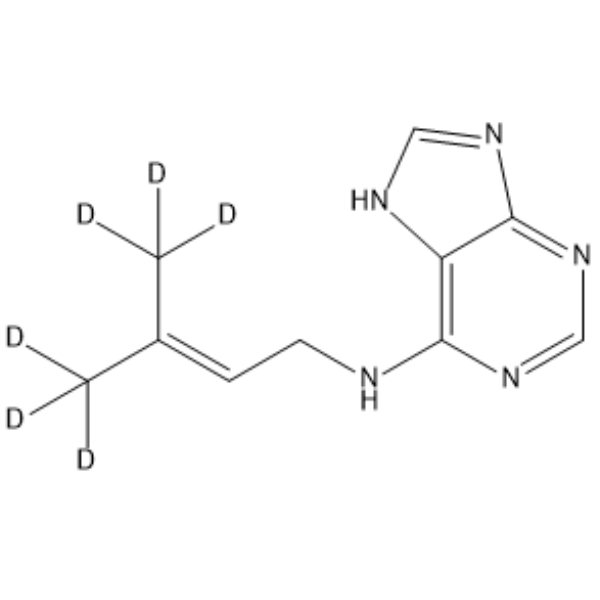
6-(γ,γ-Dimethylallylamino)purine-d6 structure
|
Common Name | 6-(γ,γ-Dimethylallylamino)purine-d6 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 175733-28-5 | Molecular Weight | 209.28 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H7D6N5 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of 6-(γ,γ-Dimethylallylamino)purine-d66-(γ,γ-Dimethylallylamino)purine-d6 is the deuterium labeled 6-(γ,γ-Dimethylallylamino)purine (HY-112103). 6-(γ,γ-Dimethylallylamino)purine is a plant growth substance[1][2]. |
| Name | 6-(γ,γ-Dimethylallylamino)purine-d6 |
|---|
| Description | 6-(γ,γ-Dimethylallylamino)purine-d6 is the deuterium labeled 6-(γ,γ-Dimethylallylamino)purine (HY-112103). 6-(γ,γ-Dimethylallylamino)purine is a plant growth substance[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. Derivative UV spectroscopic data show that the plant growth substances 6-(γ,γ-Dimethylallylamino)purine (N6-(delta 2-isopentenyl) adenine, i6Ade)and indolylacetic acid (IAA) can bind to the yeast alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) and affect coenzyme-enzyme binding. At fixed ethanol concentrations (27.8 and 111.1 mM) and varying NAD+ concentrations (0.033-2 mM), as well as at fixed levels of coenzyme (0.67 and 2 mM), and at varying concentrations of ethanol (1.4-111.1 mM), the rate of ethanol oxidation is significantly inhibited by i6Ade and IAA. The kinetics of the ADH reaction is affected by two inhibition constants (Ki and Ki') which correspond to the dissociation constants of complexes EI and ESI, respectively. For i6Ade the Ki=0.52±0.06 mM and Ki'=0.74±0.07 mM, and for IAA the Ki=0.88±0.03 mM and Ki'=0.99±0.02 mM[2]. |
| Molecular Formula | C10H7D6N5 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 209.28 |