5-Chlorouracil
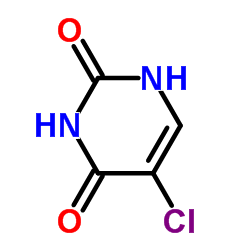
5-Chlorouracil structure
|
Common Name | 5-Chlorouracil | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1820-81-1 | Molecular Weight | 146.53 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H3ClN2O2 | Melting Point | >300 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 203.9ºC | |
Use of 5-Chlorouracil5-Chlorouracil (Fluorouracil Impurity) is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research. |
| Name | 5-chlorouracil |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 5-Chlorouracil (Fluorouracil Impurity) is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | 5-氯尿嘧啶是嘧啶核苷碱基尿嘧啶的氯化衍生物。在体内,它会转化为具有致突变性和遗传毒性的氯脱氧尿苷。1 尿嘧啶在无细胞髓过氧化物酶、过氧化物和氯化物系统中的 5 位被氯化,在该系统中形成次氯酸 2 5-氯尿嘧啶已在体外和体外用佛波醇 12-肉豆蔻酸酯 13-乙酸酯刺激的人嗜中性粒细胞中被发现从浅表感染部位分离的炎性人体渗出物。在角叉菜胶诱导的炎症大鼠模型和患者来源的人动脉粥样硬化主动脉组织中,从炎症部位分离的渗出液中 5-氯尿嘧啶的水平增加。3,4 参考资料 |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | >300 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C4H3ClN2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 146.53 |
| Flash Point | 203.9ºC |
| Exact Mass | 145.988312 |
| PSA | 65.72000 |
| LogP | -0.52 |
| Vapour Pressure | 1.98E-07mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.587 |
| InChIKey | ZFTBZKVVGZNMJR-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=c1[nH]cc(Cl)c(=O)[nH]1 |
| Storage condition | Refrigerator |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATAMUTATION DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | YQ9410000 |
| HS Code | 29335995 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 8 | |
| HS Code | 2933599090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933599090. other compounds containing a pyrimidine ring (whether or not hydrogenated) or piperazine ring in the structure. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Electron attachment to chlorouracil: a comparison between 6-ClU and 5-ClU.
J. Chem. Phys. 120 , 704-709, (2004) Low energy electron impact to the isomers 6-chlorouracil (6-ClU) and 5-chlorouracil (5-ClU) yields a variety of negative ion fragments with surprisingly high cross sections. These ions are dominantly ... |
|
|
Polymerase incorporation and miscoding properties of 5-chlorouracil.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 740-748, (2010) Inflammation-mediated hypochlorous acid (HOCl) can damage DNA, DNA precursors, and other biological molecules, thereby producing an array of damage products such as 5-chlorouracil (ClU). In this study... |
|
|
Myeloperoxidase generates 5-chlorouracil in human atherosclerotic tissue: a potential pathway for somatic mutagenesis by macrophages.
J. Biol. Chem. 281(6) , 3096-104, (2006) Somatic mutations induced by oxidative damage of DNA might play important roles in atherogenesis. However, the underlying mechanisms remain poorly understood. Myeloperoxidase, a heme protein expressed... |
| 5-Chloropyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione |
| 2,4(1H,3H)-Pyrimidinedione,5-chloro |
| 5-Chlorouracil |
| 5-chloro-2,4-dioxopyrimidine |
| 5-chloro-1H-pyrimidine-2,4-dione |
| 4-chlorouracil |
| 5-Chloro-2,4(1H,3H)-pyrimidinedione |
| EINECS 217-339-7 |
| 5-chloro-uracil |
| Uracil,5-chloro |
| 2,4(1H,3H)-Pyrimidinedione, 5-chloro- |
| 5-Chloro-2,4-dihydroxypyrimidine |
| MFCD00006019 |
| 5-Chloropyrimidine-2,4-diol |
 CAS#:66-22-8
CAS#:66-22-8 CAS#:42821-92-1
CAS#:42821-92-1 CAS#:65906-87-8
CAS#:65906-87-8 CAS#:123551-49-5
CAS#:123551-49-5 CAS#:128-09-6
CAS#:128-09-6 CAS#:106146-79-6
CAS#:106146-79-6 CAS#:50-90-8
CAS#:50-90-8 CAS#:40338-28-1
CAS#:40338-28-1 CAS#:108-24-7
CAS#:108-24-7 CAS#:64-19-7
CAS#:64-19-7 CAS#:111854-28-5
CAS#:111854-28-5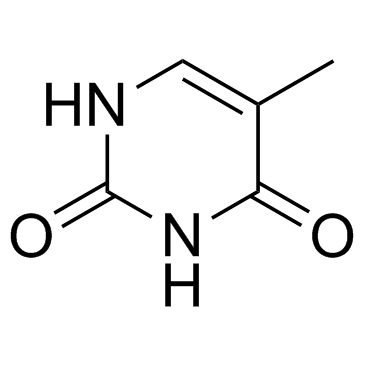 CAS#:65-71-4
CAS#:65-71-4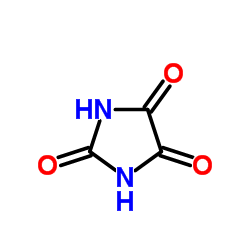 CAS#:120-89-8
CAS#:120-89-8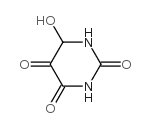 CAS#:19186-12-0
CAS#:19186-12-0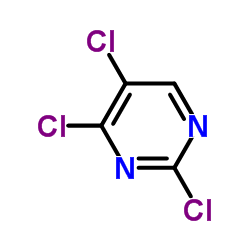 CAS#:5750-76-5
CAS#:5750-76-5 CAS#:1137-90-2
CAS#:1137-90-2 CAS#:58990-53-7
CAS#:58990-53-7
